Brown School faculty part of international obesity report
The Brown School’s Ross Hammond and Peter Hovmand are both part of the Lancet Commission on Obesity, which released its major new report Jan. 27. The main takeaway? Obesity, climate change and hunger are inextricably linked and must be fought as one challenge.
Brown School launches substance use disorder clinic
The Brown School has partnered with Preferred Family Healthcare in St. Louis to launch the Community Academic Partnership on Addiction (CAPA), a teaching, learning and research clinic aimed at addressing substance use disorder. The Brown School’s David Patterson Silver Wolf serves as CAPA’s chief research officer.
Communities that most need tobacco sales restrictions aren’t getting them, study finds
U.S. communities with higher smoking rates or lower excise taxes were less likely to adopt retail policies restricting tobacco sales, according to new research from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
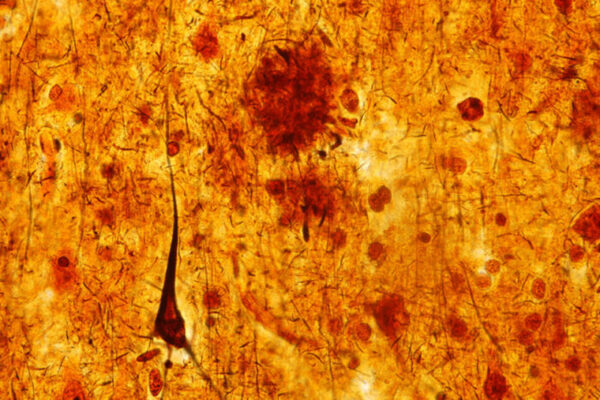
Sleep deprivation accelerates Alzheimer’s brain damage
A study in mice and people from the School of Medicine shows that sleep deprivation causes tau levels to rise and tau tangles to spread through the brain, accelerating Alzheimer’s brain damage.
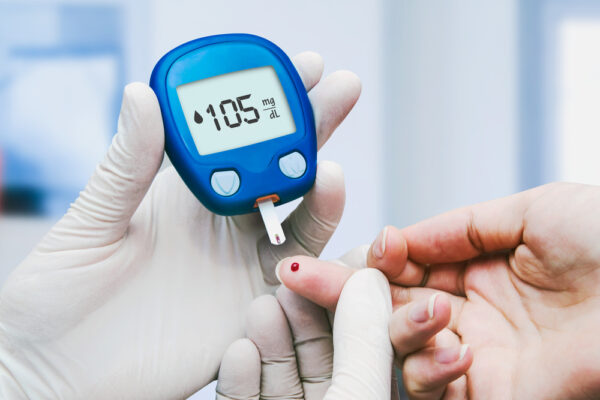
NIH grant will fund study on how communities address diabetes
The Brown School and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have received a $2.9 million grant from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases to study the impact of addressing unmet basic needs among Medicaid beneficiaries with diabetes.
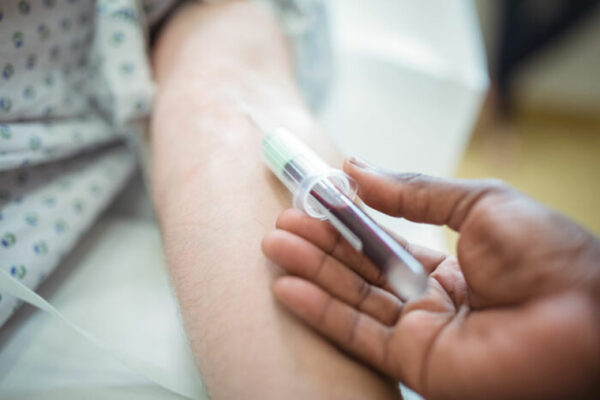
Blood test detects Alzheimer’s damage before symptoms
A simple blood test reliably detects signs of brain damage in people on the path to developing Alzheimer’s disease – even before they show signs of confusion and memory loss, according to a new study from the School of Medicine and the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases.
Serving with a clear mission
Monique Williams, AB ’95, MD ’99, MSCI ’08, is a physician with expertise in geriatric medicine and an advocate for including underrepresented populations in medical studies.
Physical Activity and Public Health Practice
Presented from both a research and a practice perspective while discussing the best available research, this book provides the basis for planning and implementing physical activity programs that work and can build healthier communities. This hands-on text incorporates learning objectives, real-world examples, case studies, and bulleted lists whenever possible so that the content can be […]
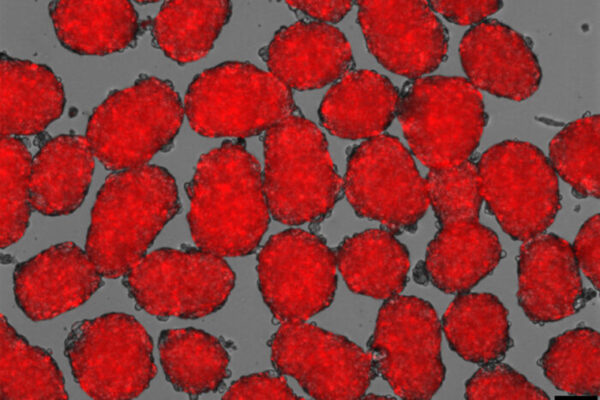
New hope for stem cell approach to treating diabetes
By tweaking the recipe for coaxing human stem cells into insulin-secreting beta cells, a team of researchers at the School of Medicine has shown that the resulting cells are more responsive to fluctuating glucose levels in the blood. The finding may lead to a new approach to treating diabetes.
Gene therapy blocks peripheral nerve damage in mice
In a new study from the School of Medicine, scientists have blocked the destruction of nerve axons in mice, a step toward helping patients with various neurodegenerative disorders.
Older Stories