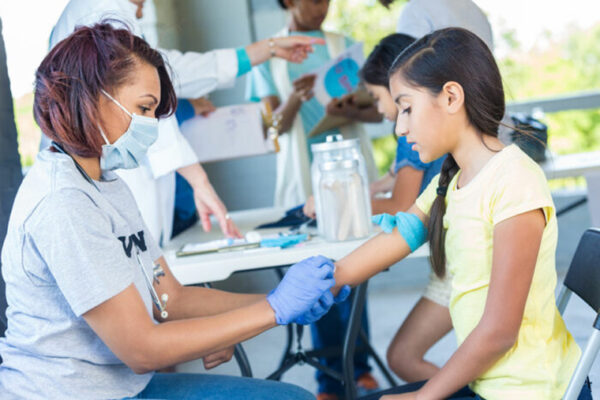
$3.4 million aids effort to make a better flu vaccine
With the aid of a grant from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases of the National Institutes of Health, School of Medicine researchers are studying why immunity elicited by the flu vaccine wanes so rapidly. The goal is a better, longer-lasting flu vaccine.
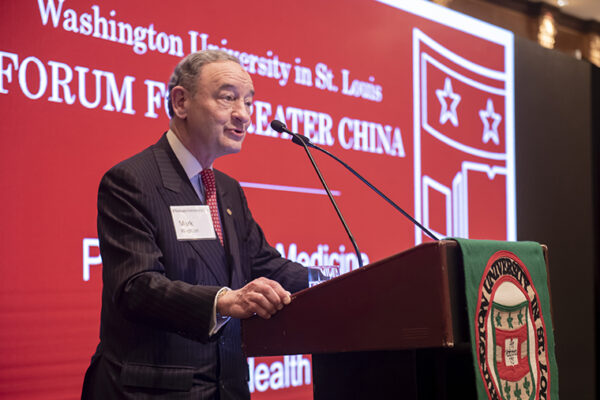
Forums for Greater China, India focus on collaborations, partnerships
A pair of events in Hong Kong and Mumbai helped to further strengthen Washington University’s impact in the Asia-Pacific region and showcase its world-leading, collaborative research.
WashU Expert: Want to stop e-cig epidemic? Don’t forget state, local policies
Tobacco control experts at Washington University in St. Louis would welcome a crackdown on e-cigarette commercials on television and radio. But advertising restrictions, as recently suggested by a member of the Federal Communications Commission, are just one way to curb the vaping epidemic among America’s youth, said Doug Luke, professor at the Brown School and director of the Center for Public Health Systems Science.
Computational biology project aims to better understand protein folding
Greg Bowman, at the Washington University School of Medicine, is leading one of the largest crowd-sourced computational biology projects in the world. Called Folding@home, it’s aimed at understanding how proteins fold into their proper shapes. Bowman understands the importance of protein folding more than most. He became legally blind by age 9 due to a condition caused when a protein doesn’t fold properly.
Unnecessary testing for UTIs cut by nearly half
Over-testing for urinary tract infections (UTIs) leads to unnecessary antibiotic use, which spreads antibiotic resistance. Infectious disease specialists at the School of Medicine made changes to hospital procedures that cut urine tests by nearly half without compromising doctors’ abilities to detect UTIs.
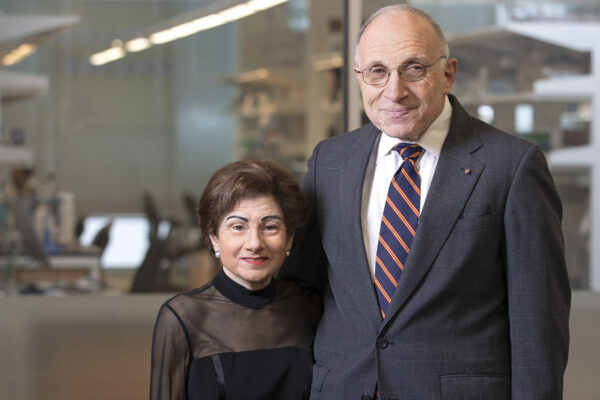
Needlemans commit $15 million aimed at therapies for chronic diseases
The School of Medicine has received a $15 million commitment from longtime benefactors Philip and Sima Needleman to support two cutting-edge research centers aimed at developing new treatments for diseases that collectively affect millions.
For adult scoliosis, surgery, other treatments are viable options
A School of Medicine study of adults with lumbar scoliosis and found that the most important factor in determining whether to do surgery is the extent of a patient’s disability due to his or her spinal deformity, as well as how much that disability interferes with day-to-day life.
Nerve transfer surgery gives hope to children with rare paralyzing illness
School of Medicine surgeon Amy Moore, MD, has performed nerve transfer surgeries on children stricken with a rare paralyzing illness called acute flaccid myelitis. Researchers believe the condition may be caused by a common enterovirus.
Less anesthesia during surgery doesn’t prevent post-op delirium
One in four older adults experiences delirium after surgery. However, School of Medicine researchers have found that closely monitoring brain activity and minimizing anesthesia if needed has no significant effect on the occurrence of delirium.
Women’s brains appear three years younger than men’s
A new study from the School of Medicine finds that women’s brains appear to be about three years younger than men’s of the same chronological age, metabolically speaking. The findings could be one clue to why women tend to stay mentally sharp longer than men.
Older Stories