Cannabis during pregnancy bumps psychosis risk in offspring
Pregnant women who use cannabis may slightly increase the risk their unborn child will develop psychosis later in life, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Rineys give $15 million to develop, test therapies for neurodegenerative diseases
The School of Medicine has received a $15 million gift from Paula and Rodger Riney aimed at accelerating research and developing new treatments for two major neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Probiotic bacteria evolve inside mice’s GI tracts
Probiotics – living bacteria taken to promote digestive health – evolve once inside the body and have the potential to become less effective and sometimes even harmful, according to a new study from the School of Medicine. The findings suggest that developers of probiotic-based therapeutics must consider how the probiotics might change after administration.
Home-based lifestyle intervention minimizes maternal weight gain
Weight gain during pregnancy and postpartum are important causes of long-term weight gain and the development of obesity-related diseases among women. A new study from Washington University in St. Louis finds providing a home-based lifestyle intervention effectively minimizes excess maternal weight gain during pregnancy and through 12-months postpartum in underserved African American women with obesity.
Medications to treat opioid addiction are effective, though not widely used
Although medications to treat opioid use disorder are safe and effective, most people who could benefit from these treatments do not receive them, finds a new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The Brown School’s David Patterson Silver Wolf was one of the authors of the report.
Obese mouse mothers trigger heart problems in offspring
Mitochondria manufacture energy in every cell of the body, including heart muscle cells. A new study from the School of Medicine shows that cardiac mitochondria are abnormal in the offspring of mouse mothers that become obese due to a high-fat, high sugar diet. Those offspring then pass on the mitochondrial defects at least two more generations.
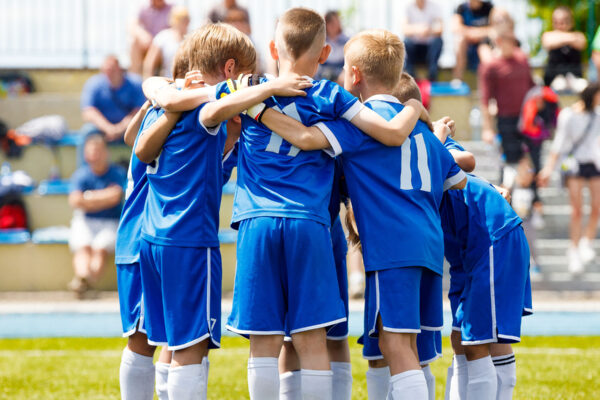
Student Gorham excels in the lab, on the track
Personal experience told Lisa Gorham, captain of the Washington University in St. Louis cross-country, track and indoor track teams, that team sports and adolescent mental health are linked. But what would the data say? Gorham has just published her findings in a leading journal — a rare accomplishment for an undergraduate researcher.
How team sports change a child’s brain
Adult depression has long been associated with shrinkage of the hippocampus, a brain region that plays an important role in memory and response to stress. Now, new research from Washington University in St. Louis has linked participation in team sports to larger hippocampal volumes in children and less depression in boys ages 9 to 11.
Topical immunotherapy keeps skin cancer risk at bay
A combination of two topical creams lowers the risk that patients will develop squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, according to new research at the School of Medicine. The combination already has been shown to clear precancerous skin lesions from sun-damaged skin.
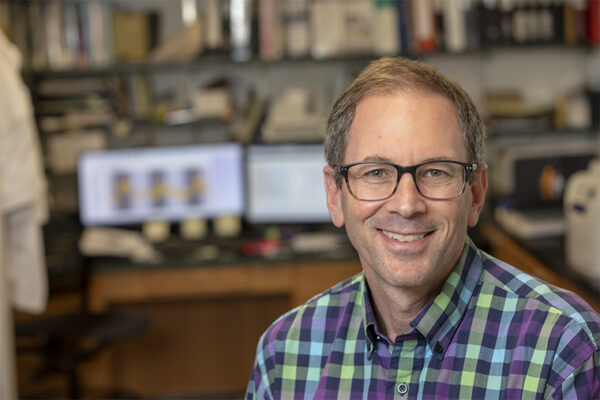
Washington People: Erik Herzog
Erik Herzog, professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, studies the molecules, cells and circuits of mammalian circadian timing. He also supports and encourages younger neuroscience researchers, from elementary school all the way through doctoral programs.
Older Stories