Safety-net hospitals fare better under new Medicare reimbursement rules
The School of Medicine has led a new study showing that new Medicare reimbursement rules reduce financial penalties for safety-net hospitals. The change shifts some of the financial burden away from hospitals that care for the most vulnerable patients.
Up to $24 million will help to eliminate two tropical diseases
An international team led by Gary Weil, MD, of the School of Medicine is poised to help eliminate two disabling tropical diseases as public health problems. A large grant from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation will fund clinical trials and other studies aimed at preventing new cases of elephantiasis and river blindness.
$10 million gift aimed at improving treatments for mental illness
Philanthropists Andrew and Barbara Taylor and the Crawford Taylor Foundation have committed $10 million to the School of Medicine to continue research to investigate the scientific underpinnings of psychiatric illnesses, with the goal of improving diagnosis and treatment.
Centene and Washington University collaborate to advance personalized medicine research
Centene Corp. and the School of Medicine announced a partnership April 8 to transform and accelerate research into treatments for Alzheimer’s disease, breast cancer, diabetes and obesity. As part of the partnership, Centene will fund up to $100 million over 10 years in research at the university.
Washington People: Robert Gereau
Robert W. Gereau, the Dr. Seymour and Rose T. Brown Professor of Anesthesiology at Washington University School of Medicine, is working to discover the genetic and molecular roots of pain, with a goal of reversing the processes that cause pain and make it so disabling.
The End of the Beginning
Cancer, Immunity and the Future of a Cure
A fascinating history of our understanding and the treatment of cancer by one of the leading figures in the field—who is also a pioneer on the cusp of a breakthrough.
‘Jumping genes’ drive many cancers
Mistakes in DNA are known to drive cancer growth. But a new study, from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, heavily implicates a genetic phenomenon commonly known as “jumping genes” in the growth of tumors.
WashU Expert: What happens if ACA is eliminated?
The Trump administration said this week that the whole Affordable Care Act should be struck down in the courts. Doing so would have profound implications on health care and the economy, says an expert on health economics at Washington University in St. Louis.
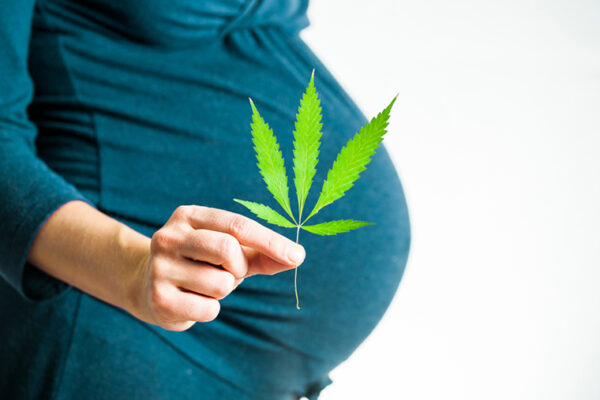
Cannabis during pregnancy bumps psychosis risk in offspring
Pregnant women who use cannabis may slightly increase the risk their unborn child will develop psychosis later in life, suggests new research from Washington University in St. Louis.
Rineys give $15 million to develop, test therapies for neurodegenerative diseases
The School of Medicine has received a $15 million gift from Paula and Rodger Riney aimed at accelerating research and developing new treatments for two major neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
Older Stories