More cancer patients get help to quit smoking
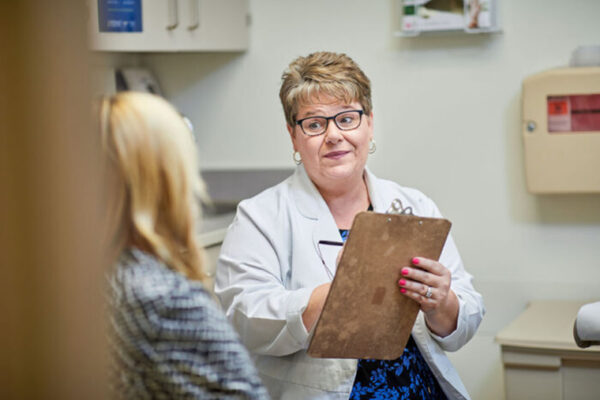
A new program funded through the Cancer Moonshot Initiative has doubled the number of patients at Siteman Cancer Center assessed for smoking — and increased by fivefold the percentage of cancer patients who smoke now taking medication to help them quit. The results have been published in the journal Translational Behavioral Medicine.
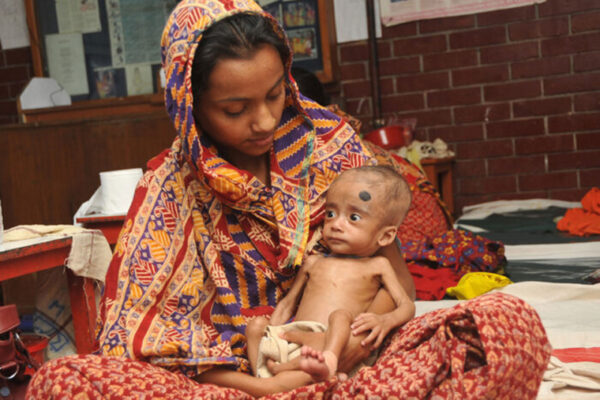
For malnourished children, new therapeutic food boosts gut microbes, healthy development
Researchers at the School of Medicine and the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research in Dhaka, Bangladesh, are developing a new approach to address childhood malnutrition. They are designing therapeutic foods aimed at repairing the gut microbiomes of malnourished children.
Fighting pancreatic cancer with immunotherapy
Researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis and Rush University in Chicago have found a compound that promotes a vigorous immune assault on pancreatic cancer. The findings, in mice, suggest a way to improve immunotherapy for the deadly disease in patients.
Theater production explores wonders of human brain
Two nationally renowned neurosurgeons at the School of Medicine will present BrainWorks, a live theatrical performance that explores the wonders of the human brain by dramatizing real-life neurological cases. The performance, comprised of four one-act plays, will debut July 19-21.
Flatlining
Race, Work, and Health Care in the New Economy
African American health care workers are there for a reason. A new book by a Washington University in St. Louis social scientist shows how hospitals, clinics and other institutions participate in “racial outsourcing,” relying heavily on black doctors, nurses, technicians and physician assistants to do “equity work” — extra labor that makes organizations and their services […]
Understanding how tics are suppressed may help some at risk for tic disorders
Studying children shortly after they began experiencing tics, researchers at the School of Medicine discovered that although tics don’t go away, most children are able to suppress and control them. Understanding how they do that may provide insight to help others at risk for significant tic disorders.
Alzheimer’s missing link ID’d, answering what tips brain’s decline
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that immune cells that typically protect neurons from damage may be the link between such early and late brain changes in Alzheimer’s disease. Breaking that link could lead to new approaches to delay or prevent the disease.
Treatment for common cause of diarrhea more promising
School of Medicine researchers have figured out how to grow the intestinal parasite Cryptosporidium in the lab, an achievement that will speed efforts to treat or prevent diarrhea caused by the parasite.
Emotional violence in childhood, adolescence associated with suicidal thoughts
Early exposure to emotional violence “significantly” increases the chances that youths will contemplate suicide, according to new research from three countries conducted by the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Helping schools with suicide prevention
With the goal of preventing youth suicide by helping schools set up a student support system, the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis hosted the Hope Policy Academy June 6.
Older Stories