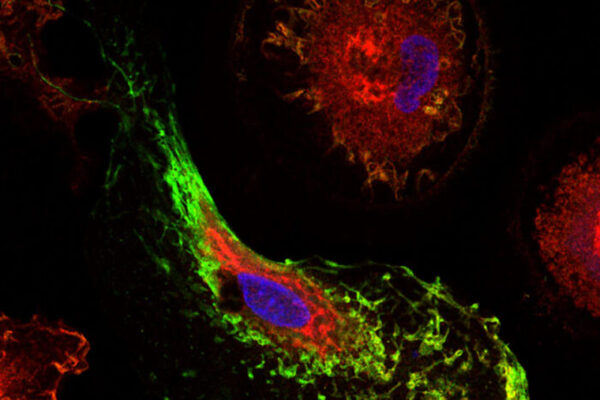
Arthritis-causing virus hides in body for months after infection
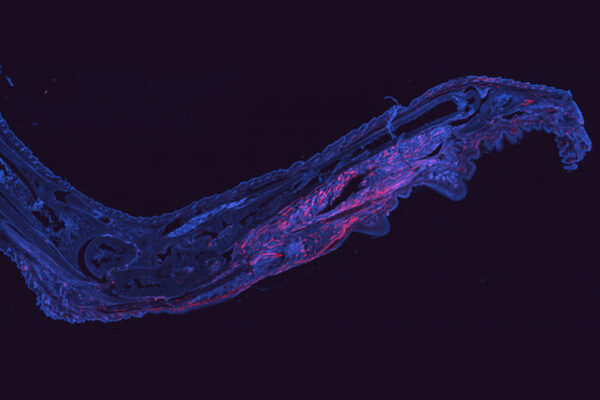
Researchers at the School of Medicine have developed a way to fluorescently tag cells infected with chikungunya virus. The technique opens up new avenues to study how the virus persists in the body and potentially could lead to a treatment.
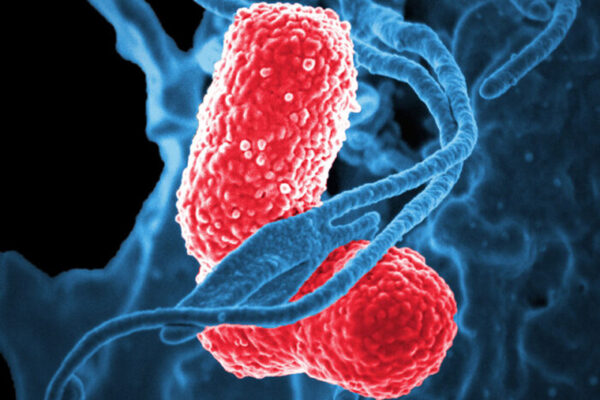
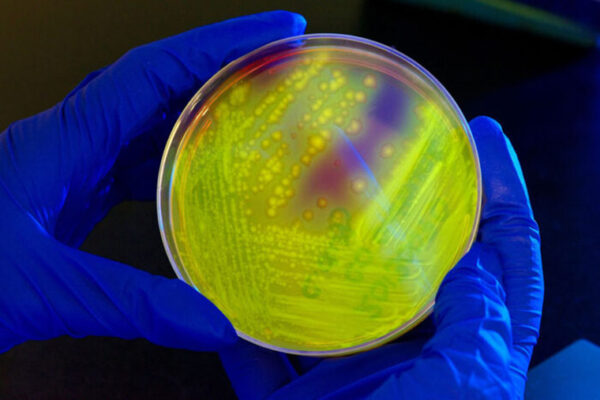
Vaccine against deadly superbug Klebsiella effective in mice
Researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis and the biotech startup VaxNewMo have developed a vaccine that is effective, in mice, against hypervirulent strains of Klebsiella that can cause life-threatening infections in healthy adults.
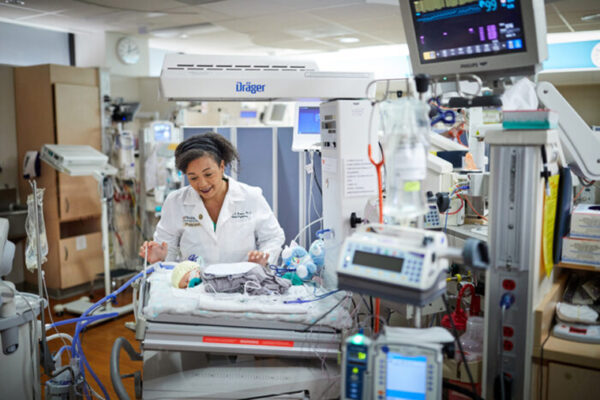
Stable home lives improve prospects for preemies
A new School of Medicine study has found that as premature babies grow, their mental health may be related less to medical challenges they face after birth than to the environment the babies enter once they leave the newborn intensive care unit.
$15 million supports quest for personalized leukemia therapies
Investigators at Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have been awarded a $15 million grant to better understand the genetic changes that drive acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a deadly blood cancer, and predict patients’ responses to therapy. The findings also may enable investigators to develop more effective therapies tailored to patients, based on the genetic characteristics of their cancer cells.
Why initial UTIs increase susceptibility to further infection
Researchers at the School of Medicine have discovered that an initial urinary tract infection (UTI) triggers changes to immune and other cells in the bladder that can prime the bladder to overreact to bacteria, worsening subsequent UTIs.
Children with mild asthma can use inhalers as needed
A new study from the School of Medicine finds that African American children with mild asthma can take their steroid inhalers as needed, based on symptoms, rather than at set times daily regardless of symptoms.
Genes linked to Alzheimer’s risk, resilience ID’d
A team led by researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified a pair of genes that influence risk for Alzheimer’s disease. The genes — known as MS4A4A and TREM2 — affect the brain’s immune cells. They influence Alzheimer’s risk by altering levels of TREM2, a protein that is believed to help microglia cells clear excessive amounts of the Alzheimer’s proteins amyloid and tau from the brain.
Gut makeup could make diarrhea less likely
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found the molecular signature of a healthy gut microbial community – the kind that can keep the intestinal bacteria Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) from overgrowing and causing diarrhea.
Rethinking seizures associated with cardiac disease
Research from Washington University in St. Louis finds that mutations of a gene implicated in long QT syndrome in humans may trigger seizures because of their direct effects on certain classes of neurons in the brain — independent from what the genetic mutations do to heart function. The new work from Arts & Sciences was conducted with fruit flies and is published August 8 in PLOS Genetics.
Medicare drug plan’s design keeps federal subsidies in check
In a new study involving a researcher from Washington University in St. Louis’ Olin Business School, the co-authors discovered something they say surprised them: Medicare Part D’s setup actually inhibits insurers from seeking higher subsidies from the government. It keeps subsidies in check by virtue of the way it’s designed.
Older Stories