Families with long, healthy life spans focus of $68 million grant
With the help of a grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers at the School of Medicine are leading the Long Life Family Study, which includes several generations of families with unusual concentrations of long-lived individuals. The goal is to uncover genetic factors that play roles in long life spans.
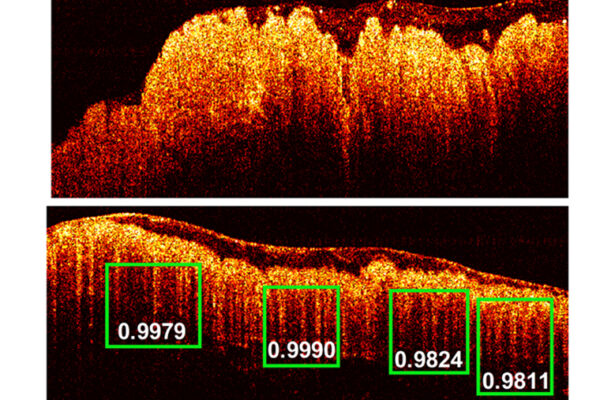
Machine learning, imaging technique may boost colon cancer diagnosis
Researchers at the McKelvey School of Engineering have devised a new imaging technique based on a technology that has been used for two decades in ophthalmology that can provide accurate, real-time, computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal cancer.
Why health insurance in rural communities is so expensive
Small risk pools may contribute to the challenges faced by private insurance plans in rural areas, in which case risk reinsurance, or insurance for the insurer, is a potential policy solution, finds a new study from the Brown School at Washington University in St. Louis.
Halting opioid abuse aim of several grants from NIH, CDC
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received federal grants totaling more than $10 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). The grants are part of a nationwide push to fund research targeting the opioid epidemic.
Drug-resistant staph can spread easily in household environments
New research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis sheds light on how the superbug methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is introduced into households and how it can spread among family members.
New book examines eating disorders, failure to care for those impacted
A new book from Washington University in St. Louis cultural anthropologist Rebecca Lester explores eating disorders — a topic that impacts and kills almost as many people in the United States as the opioid crisis yet receives a fraction of the sympathy, support or funding.
Gut microbes alter characteristics of norovirus infection
A new School of Medicine study reveals details about how gut microbes interact with norovirus infection in the mouse gut. The research opens up new ways of thinking about potential therapies for this intestinal infection.
Brain imaging of babies with Down syndrome focus of $11.5 million grant
School of Medicine researchers have received an $11.5 million grant to lead a multicenter effort to understand how brain development in babies with Down syndrome differs from that in other babies. The effort will provide a foundation that may lead to therapies to counter developmental delays in children with the condition.
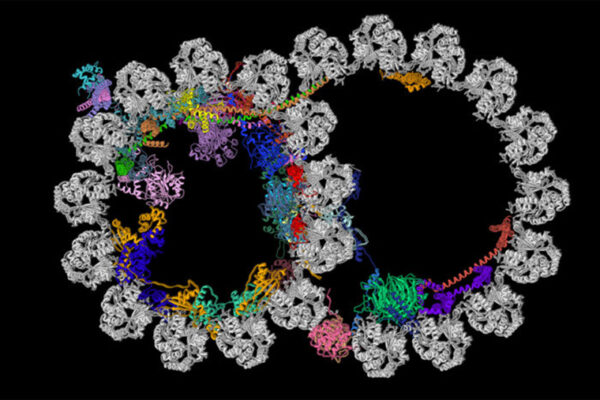
Scientists unravel mysteries of cells’ whiplike extensions
Scientists at the School of Medicine and Harvard have revealed the first detailed look at the inner structure of cilia. Cilia perform diverse tasks required to keep the body healthy, but when these whiplike appendages on cells malfunction, the consequences can be devastating.
Famished
Eating Disorders and Failed Care in America
When Rebecca Lester was eleven years old — and again when she was eighteen — she almost died from anorexia nervosa. Now both a tenured professor in anthropology and a licensed social worker, she turns her ethnographic and clinical gaze to the world of eating disorders — their history, diagnosis, lived realities, treatment and place […]
Older Stories