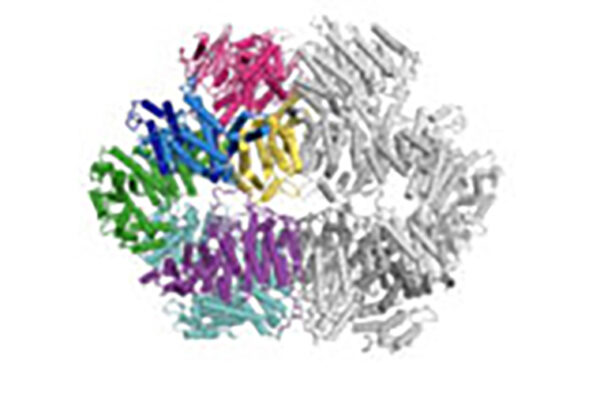
Lethal brain infections in mice thwarted by decoy molecule
School of Medicine scientists have identified a molecule that protects mice from brain infections caused by Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus, a mosquito-borne virus notorious for causing fast-spreading, deadly outbreaks in Mexico, Central America and northern South America.
Study: Respiratory failure in COVID-19 usually not driven by cytokine storm
A study led by School of Medicine researchers showed that, contrary to expectations, most people with severe COVID-19 do not suffer from unbridled inflammation. The findings suggest that anti-inflammatory therapies may not be helpful for most COVID-19 patients.
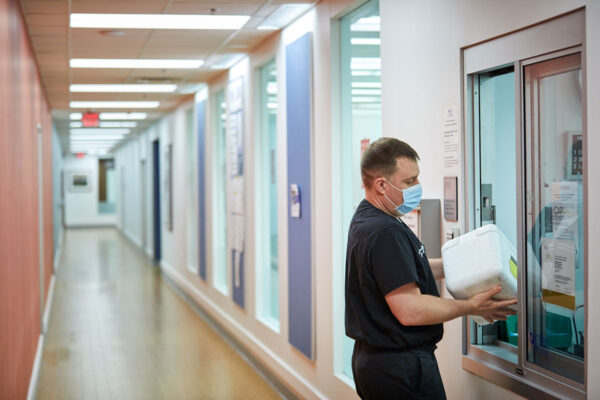
Fluvoxamine may prevent serious illness in COVID-19 patients
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found that the drug fluvoxamine may help prevent deterioration in COVID-19 patients, making hospitalization less likely.
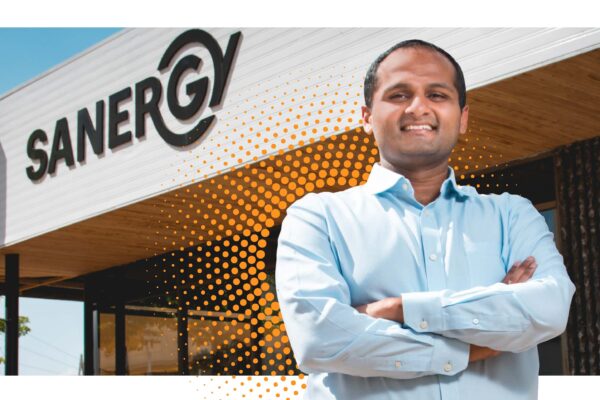
Sustainable sanitation
Alumnus Ani Vallabhaneni is co-founder of Sanergy, an organization employing systems-based solutions to solve urban sanitation challenges — and transforming lives in the process.
For all ages
What would a truly intergenerational community look like? Three WashU scholars explain how a community can become more accessible for people of every age.
Making cancer cells more susceptible to dying
Cancer cells can survive even after being hit with high doses of chemotherapy or radiation, but a School of Medicine team working to make treatment more effective is focusing on ways to tweak the inner machinery of cancer cells to make them more susceptible to dying.
Improving emergency care for people with dementia is focus of new grant
Washington University School of Medicine is one of four institutions to receive a National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant to study how to improve emergency care for adults with dementia. For the project, experts in emergency medicine, geriatrics and dementia will identify and address gaps in emergency care.
Cornea appears to resist infection from novel coronavirus
Although viruses such as herpes simplex can infect the eye’s cornea and Zika virus has been found in corneal tissue and tears, new School of Medicine research suggests the cornea can resist infection from the novel coronavirus.
Research Methods for Public Health
This book presents information on research methods in a way that is complementary to other public health coursework. Epidemiology digs deep into specific methods for identifying distribution and determinants of health issues. An understanding of basic research methods serves as a foundation for mastery of epidemiology. Biostatistics is another component of public health preparation. The […]
New insight into how brain neurons influence choices
By studying animals choosing between drink options, School of Medicine researchers have found that the activity of certain neurons in the brain leads directly to the choice of one option over another. The findings could lead to better understanding of how decision-making goes wrong in conditions such as addiction and depression.
Older Stories