Roediger honored for leadership, research contributions
The American Psychological Association has named Henry L. “Roddy” Roediger, the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor of Psychological & Brain Sciences in Arts & Sciences, the recipient of its 2021 Award for Distinguished Scientific Contributions. In addition, the Psychonomic Society has awarded Roediger the Clifford T. Morgan Distinguished Leadership Award.
Don receives award from pediatric radiology society
Steven Don, MD, associate professor of radiology and of pediatrics at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the 2020 Pioneer Award from the Society for Pediatric Radiology for his innovative work in the development of digital radiography and digital imaging.
Researchers to work with parents, teachers on COVID-19 testing communications
Researchers at the Brown School are conducting discussion groups with parents and staff in the Special School District of St. Louis County to develop communication tools surrounding COVID-19 testing and vaccination. The research is funded by a two-year, $5 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to the Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis to offer 50,000 saliva tests to students, teachers and staff in the six special education schools operated by the district.
Brown School group to study COVID-19 disparities with $1.5M grant
The Brown School’s Health Communication Research Laboratory has received two grants totaling $1.57 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to understand and address COVID-19 health disparities.
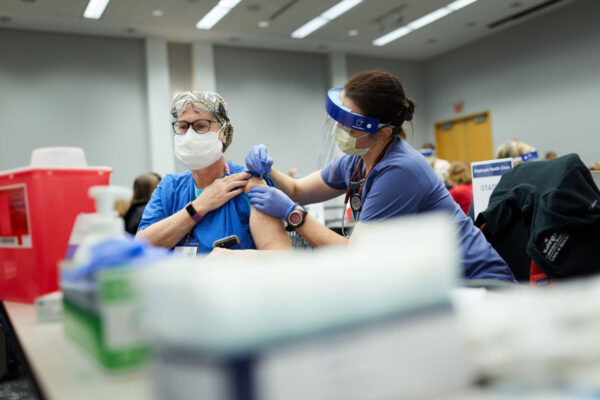
Historic, hopeful moment arrives on Medical Campus
As part of a historic effort to end the COVID-19 pandemic, health-care personnel at the School of Medicine and BJC HealthCare have begun receiving the first doses of a vaccine against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Protein involved in removing Alzheimer’s buildup linked to circadian rhythm
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have discovered a protein that links the amyloid-removal process to the circadian clock. The protein, YKL-40, could help explain why people with Alzheimer’s frequently suffer from sleep disturbances — and provide a new target for Alzheimer’s therapies.
Chaudhuri receives V Scholar Award
Aadel A. Chaudhuri, MD, PhD, assistant professor of radiation oncology at Washington University School of Medicine, has received the V Scholar Award from the V Foundation for Cancer Research.
Eric W. Carson
At the School of Medicine, orthopedic surgeon Eric W. Carson aims to increase diversity and mentorship in medicine.
COVID-19 patients at higher risk of death, health problems than those with flu
A deep dive into federal medical data, conducted by researchers at the School of Medicine, found that COVID-19 is much deadlier and causes more health problem for patients than the seasonal flu does.
Luby honored for advancing understanding of brain, behavior disorders
Joan L. Luby, MD, the Samuel and Mae S. Ludwig Professor of Psychiatry at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received the Ruane Prize for Child & Adolescent Psychiatry from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation.
Older Stories