Scientists to explore whether anti-inflammatory drugs control blood sugar
School of Medicine researchers have received a grant to investigate whether immunosuppressive drugs prescribed for inflammatory bowel disease or psoriasis also can control blood sugar levels.
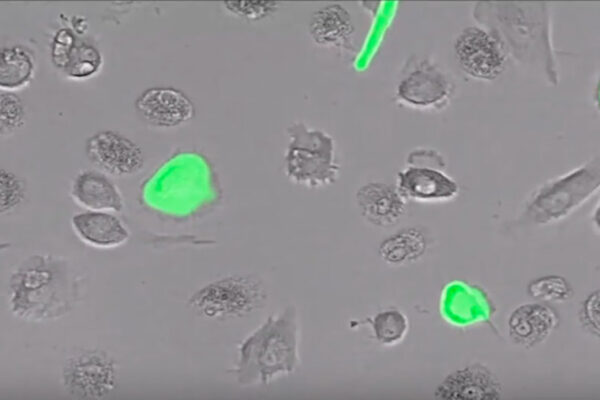
Human immune cells have natural alarm system against HIV
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis describes a strategy that could lead to therapies for clearing HIV infection. The researchers showed that human immune cells have a natural alarm system that detects the activity of a specific HIV protein.
Faculty receive grant for heart health research
Weikai Li, along with Michael J. Greenberg, both at the School of Medicine, and Michael L. Gross, in Arts & Sciences, received a three-year $750,000 grant from American Heart Association for their research titled “Interdisciplinary structural studies of iron homeostasis in cardiovascular health.”
Law clinic’s work inspires federal bill
The School of Law’s Interdisciplinary Environmental Clinic’s 2019 report “Environmental Racism in St. Louis” is helping to shape new federal legislation.
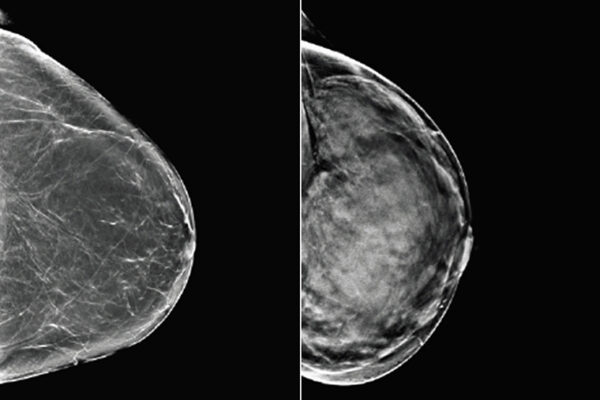
Algorithm analyzes mammograms, signals need for more breast cancer screening
Researchers at the School of Medicine and Whiterabbit.ai have developed a software that assesses breast density and can help identify women who could benefit from additional screening.
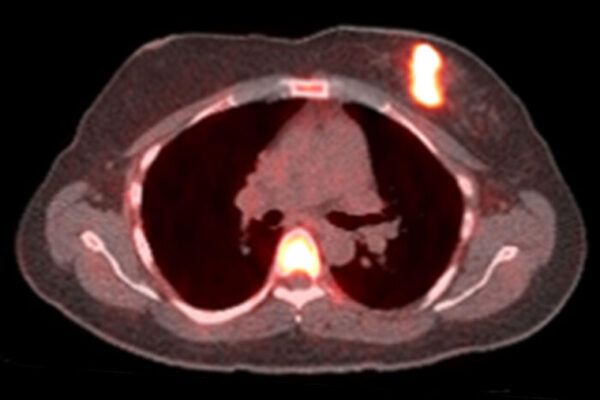
Imaging identifies breast cancer patients unlikely to benefit from hormone therapy
In a small study, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine found that only women whose tumors responded to estrogen challenge benefited from hormone therapy. The findings could help doctors choose the treatments most likely to help their patients.
Research proposals to address COVID-19 challenges sought
Washington University’s McDonnell International Scholars Academy and Social Policy Institute seek proposals from WashU researchers and their international partners to identify and address the challenges of COVID-19 through artificial intelligence, technology and big data. Proposals are due Feb. 26.
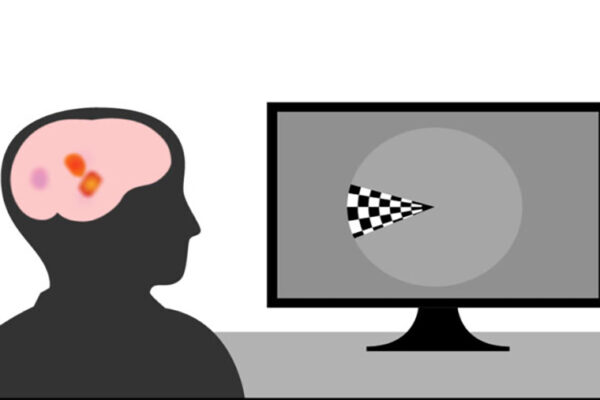
Brain signals decoded to determine what a person sees
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have used light to decode brain signals and identify what image a person sees. It could be a step toward helping people who are unable to express themselves because of brain injury or disease communicate.
Risk analysis helps contend with uncertainty of in-person activities
People now have access to better real-time information about COVID-19 infection and transmission rates, but they still have to decide what is safe to do. A new model co-authored by mathematician John McCarthy in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis helps to contend with the uncertainty.
‘Smart’ cartilage cells programmed to release drugs when stressed
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have engineered cartilage cells to release an anti-inflammatory drug in response to stresses such cells undergo when they are compressed during weight bearing and movement.
Older Stories