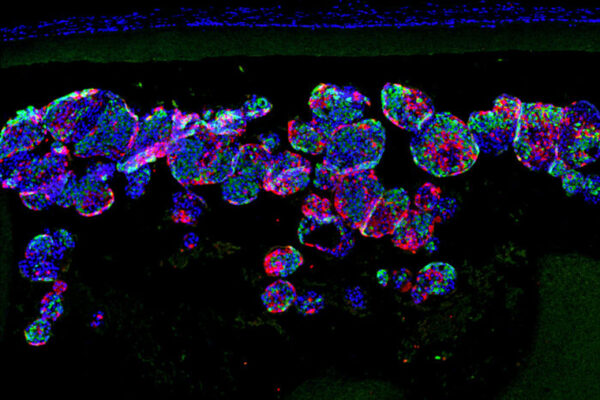
Tiny implant cures diabetes in mice without triggering immune response
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and Cornell University have implanted insulin-secreting cells into diabetic mice to normalize their blood sugar.
Synthetic data mimics real health-care data without patient-privacy concerns
Washington University investigators now have access to a new research tool that allows them to conduct clinical studies using synthetic patient data. Synthetic data produced by the new tool, called MDClone, accurately mimics real patient data without the privacy concerns.
Without requiring vaccines, filled stadiums are unsafe
“If vaccines or negative COVID-19 tests are required for attendees, 100% attendance is safe,” says the Washington University in St. Louis mathematician who helped derive the model used for fan-attendance risk analysis across many of America’s sports venues. “Without requiring vaccinations or testing, it’s not.”
Burgers receives $3.5M NIH grant
Peter M. Burgers, at the School of Medicine, received a five-year $3.5 million renewal grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for his research titled “Mechanisms of DNA replication and maintenance in eukaryotes.”
New tool activates deep brain neurons by combining ultrasound, genetics
A multidisciplinary team at Washington University led by Hong Chen has developed a new brain stimulation technique using focused ultrasound that is able to turn specific types of neurons in the brain on and off and precisely control motor activity without surgical device implantation.
Delaying lung cancer surgery associated with higher risk of recurrence, death
New research from Washington University School of Medicine has found that postponing lung cancer surgery for more than 12 weeks from the date of diagnosis with a CT scan is associated with a higher risk of recurrence and death.
Researchers keep international COVID-19 projects moving forward
Despite the pandemic, Washington University researchers collaborating with international colleagues continue to innovate and move their research forward.
Brain tumors caused by normal neuron activity in mice predisposed to such tumors
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and Stanford University have found that normal exposure to light can drive the formation and growth of optic nerve tumors in mice — and maybe people — with a genetic predisposition. Such tumors can lead to vision loss.
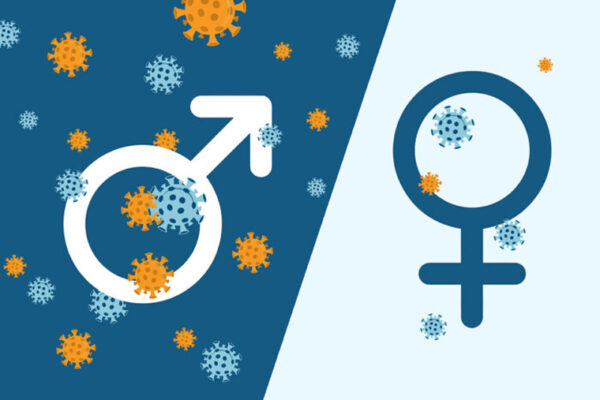
For men, low testosterone means high risk of severe COVID-19
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that, among men, low testosterone levels in the blood are linked to more severe COVID-19.
Humphreys named vice president of research society for physician-scientists
Benjamin D. Humphreys, MD, PhD, director of the Division of Nephrology at Washington University School of Medicine, has been named vice president of the American Society for Clinical Investigation, a medical honor society that advances research by physician-scientists.
Older Stories