Research to explore how genes, other factors affect cardiometabolic disease risk
With an $8.8 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers at Washington University School of Medicine will study how an individual’s risks of cardiometabolic diseases are influenced by the interaction of specific genes with demographic and lifestyle factors.
‘Good cholesterol’ may protect liver
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that a type of “good cholesterol” called HDL3, when produced in the intestine, protects the liver from inflammation and injury.
Promoting physical activity is key to achieving U.N. Sustainable Development Goals
New evidence supports the integration of physical activity promotion strategies as a key part of the action plan for achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals, finds a new study led by Brown School researchers.
New snack foods nurture healthy gut microbiome
Researchers at the School of Medicine have identified ingredients for snack food prototypes that have been formulated to deliberately change the gut microbiome in ways that can be linked to health.
Lang named to national child health advisory council
Catherine Lang, professor of physical therapy at the School of Medicine, has been appointed to serve on a national child health council for the Eunice Kennedy Schriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Iannotti speaks during UN nutrition event
Lora Iannotti, associate professor at the Brown School and an expert on maternal and child nutrition, spoke during a panel discussion in June about the launch of the UN Nutrition discussion paper on livestock-derived foods and sustainable healthy diets.
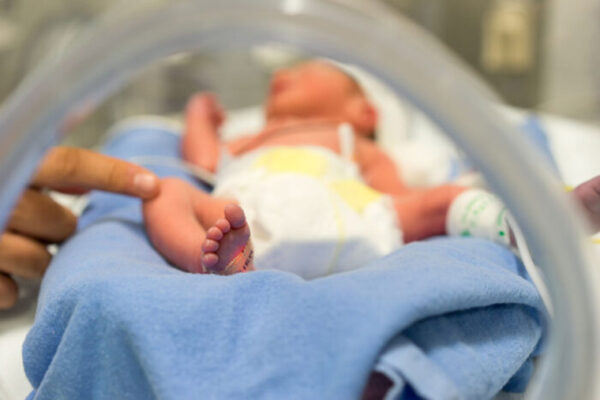
Immune system protein may defend against deadly intestinal disease in babies
A study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine has identified a protein in the immune system that may protect babies from necrotizing enterocolitis, a leading cause of death among premature infants.
Tiny implant cures diabetes in mice without triggering immune response
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine and Cornell University have implanted insulin-secreting cells into diabetic mice to normalize their blood sugar.
Western diet may increase risk of gut inflammation, infection
Eating a Western diet impairs the gut’s immune system in ways that could increase risk of infection and inflammatory bowel disease, according to a study from the Washington University School of Medicine and Cleveland Clinic.
Gordon study on childhood malnutrition honored for its impact
The Clinical Research Forum, a nonprofit association of top clinical research experts from the nation’s leading academic health centers, has awarded an international interdisciplinary team led by Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, a Distinguished Clinical Research Achievement Award for his study “Integrating Global Health with the Microbiome.”
Older Stories