Antibiotic treatment in malnourished children improves gut microbiome development
A new study led by Gautam Dantas, at the School of Medicine, shows that the concerns of increasing antibiotic resistance have merit but that the long-term benefits may outweigh the short-term risks. The findings were published Oct. 19 in The Lancet Microbe.
Fiber from crustaceans, insects, mushrooms promotes digestion
Crustaceans, insects and mushrooms are rich sources of the dietary fiber chitin, which activates the immune system and benefits metabolism, according to a new study, in mice, led by researchers at the School of Medicine.
Achieving sustainable diets with nutrition equity
One of the planet’s greatest challenges is nourishing all of humanity while protecting the health of the planet itself. In a commentary published in the journal One Earth, Lora Iannotti, a professor at the Brown School, discusses how nutrition equity for vulnerable groups is vital in this effort.
In battling obesity and prediabetes, combining exercise with weight loss is key
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that combining regular exercise with a 10% loss of body weight more than doubles sensitivity to insulin, offering important health benefits.
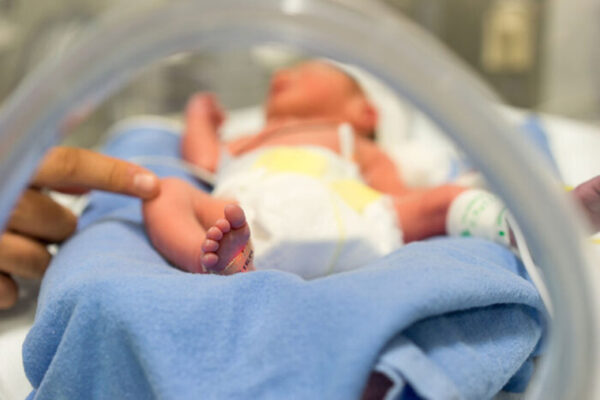
Bloodstream infections in preemies may originate from their gut microbiomes
A new study from the School of suggests that some dangerous bloodstream infections in premature infants may be caused by strains of bacteria already lurking in their gut microbiomes.
‘Motivated by hope and humility’
Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, explores the “vast, mysterious world” of the microbiome to find solutions to promote healthy growth in malnourished children. In recognition of his groundbreaking work, Gordon received the 2022 Dr. Paul Janssen Award for Biomedical Research.
WashU research spurs changes to global guidelines for feeding malnourished kids
Results of a major clinical trial in Africa led by Mark Manary, MD, at Washington University School of Medicine, have prompted a change in global guidelines for therapeutic food.
Luke contributes to new report on U.S. dietary guidelines
Douglas Luke, the Irving Louis Horowitz Professor in Social Policy at the Brown School, was part of a National Academies of Science committee that reviewed how federal dietary guidelines are developed.
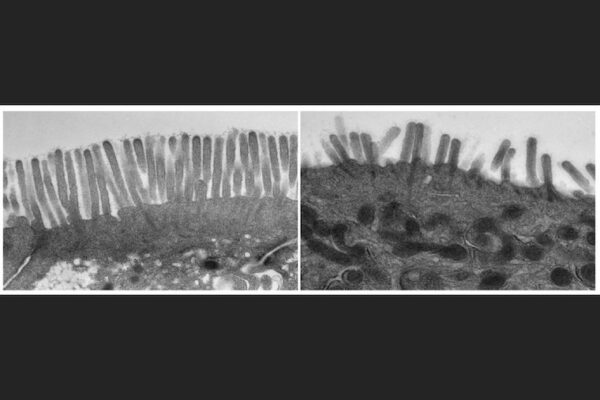
Some forms of childhood malnutrition, stunting may be preventable with vaccines
Researchers at the School of Medicine have discovered that vaccinating mice against a bacterial toxin produced by E. coli can prevent intestinal damage. The finding suggests new ways to prevent malnutrition and stunting in children.
Researchers bring Body U to schools with HHS grant
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services has awarded researchers Ellen Fitzsimmons-Craft and Denise Wilfley a grant to help improve outcomes for eating disorders in adolescent girls.
Older Stories