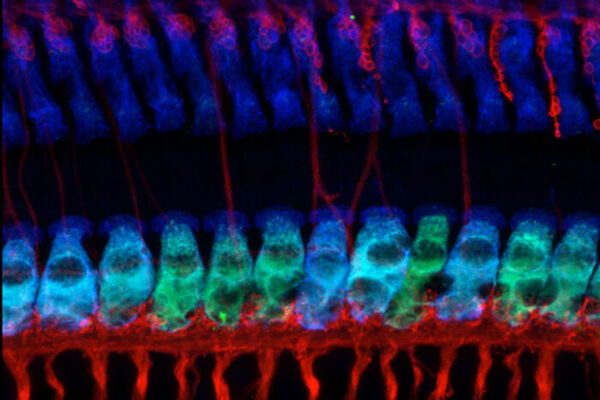
Noise-induced hearing loss blocked with drug compound
Studying mice, researchers at the School of Medicine and their colleagues have shown that a drug compound can block damage caused by too much glutamate signaling, raising the possibility of medication that prevents noise-induced hearing loss.
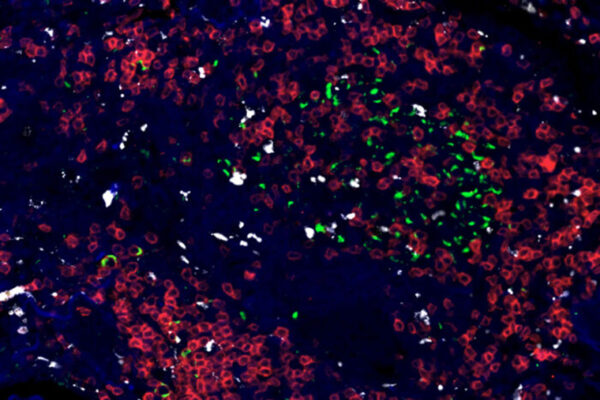
Immune responses to tuberculosis mapped across 3 species
A new study led by the School of Medicine lays out a genetic road map of immune responses to tuberculosis (TB) infection across three species.
1 in 4 kids who get antibiotics in children’s hospitals are prescribed the drugs incorrectly
New research led by the School of Medicine indicates that 1 in 4 of the children given antibiotics in U.S. children’s hospitals are prescribed the drugs inappropriately. The overuse of antibiotics poses an increasing threat to children who develop — or already have — drug-resistant infections.
Miller receives international innovation prize
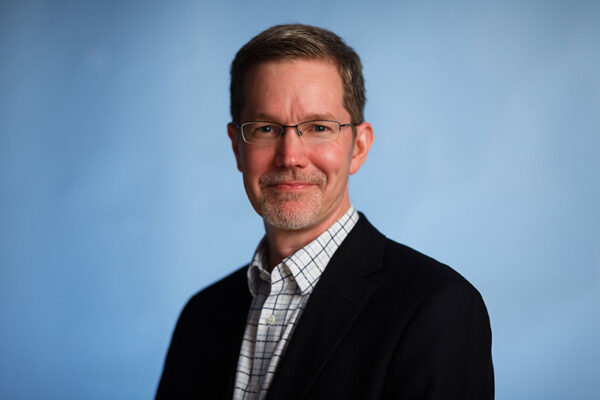
Timothy Miller, MD, PhD, the David Clayson Professor of Neurology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, and a group of his colleagues have received the inaugural Healey Center International Prize for innovation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) research from the Sean M. Healey & AMG Center for ALS at Massachusetts General Hospital.
High-protein diets boost artery-clogging plaque, mouse study shows
High-protein diets may help people lose weight and build muscle, but a School of Medicine study in mice suggests they also lead to more plaque in the arteries. The findings also show that high-protein diets spur unstable plaque, the kind most prone to rupturing and causing blocked arteries.
‘Jumping genes’ help stabilize DNA folding patterns
New School of Medicine research indicates that “jumping genes” play a surprising role in stabilizing the 3D folding patterns of the DNA molecule inside a cell’s nucleus.
Celebrating the newest National Academy of Inventors fellows
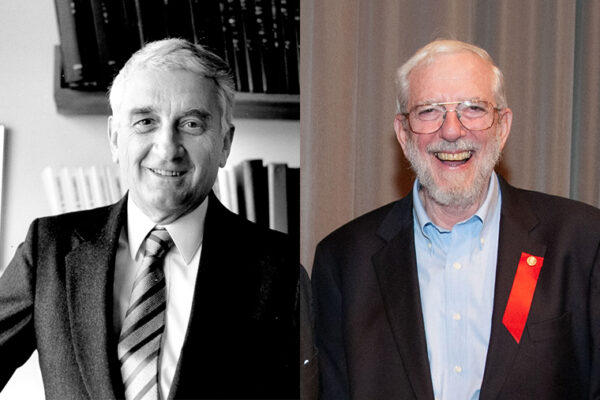
Washington University’s Jerome Cox and Jack H. Ladenson join a small but distinguished group of fellows of the National Academy of Inventors, the highest professional distinction accorded solely to academic inventors.
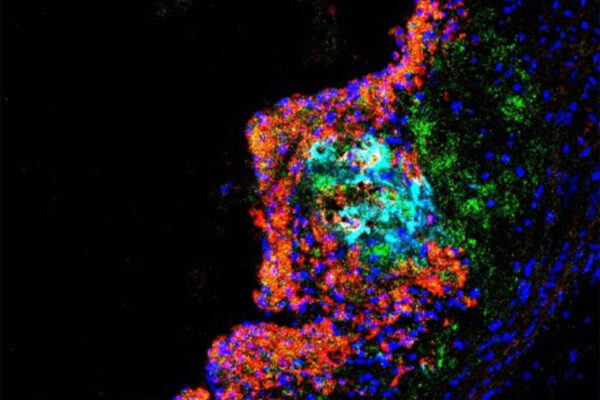
Scientists find way to supercharge protein production
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found a way to increase protein production up to a thousandfold, a discovery that could aid production of proteins used in the medical, food, agriculture, chemical and other industries.
Depression, anxiety may hinder healing in young patients with hip pain
New School of Medicine research suggests that physicians evaluating young patients with hip pain should consider more than physical health. They also should consider screening for clinical depression and anxiety — impairments that can have a negative impact on outcomes following hip surgery.
In transfusions for children, fresh and older blood are equally effective
An international study led by the School of Medicine and CHU Sainte-Justine hospital in Montreal has found no benefit in using fresh red blood cells that have been stored for up to seven days in blood transfusions for critically ill children, compared with using older red blood cells stored for nearly four weeks.
Older Stories