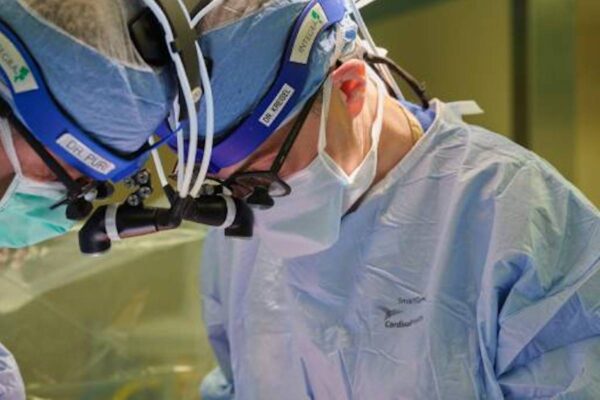
$10 million in grants aimed at preventing organ rejection after transplantation
Transplant surgeons and researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have received two grants totaling $10 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study how immune cells contribute to organ rejection, with the aim of improving the viability of organs after transplant.
Divided Bodies
Lyme Disease, Contested Illness, and Evidence-Based Medicine
In Divided Bodies, Abigail A. Dumes offers an ethnographic exploration of the Lyme disease controversy that sheds light on the relationship between contested illness and evidence-based medicine in the United States.
Study provides insight on how to build a better flu vaccine
Repeated exposure to influenza viruses may undermine the effectiveness of the annual flu vaccine. A team of researchers led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has developed an approach to assess whether a vaccine activates the kind of immune cells needed for long-lasting immunity against new influenza strains. The findings could aid efforts to design an improved flu vaccine.
Genetic mutations may be linked to infertility, early menopause
Researchers at the School of Medicine have identified a gene that plays an important role in fertility across multiple species. The study could have implications for understanding human infertility and early menopause.
Washington University develops COVID-19 saliva test
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has developed a saliva-based test for COVID-19 that is faster and easier than the swab tests currently in use. The test could help simplify and expand the availability of COVID-19 diagnostic testing across broad populations.
African American children with autism experience long delays in diagnosis
A study led by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine details the nature of delays in autism diagnoses for African American children. Such delays can result in significant consequences for young children and their families.
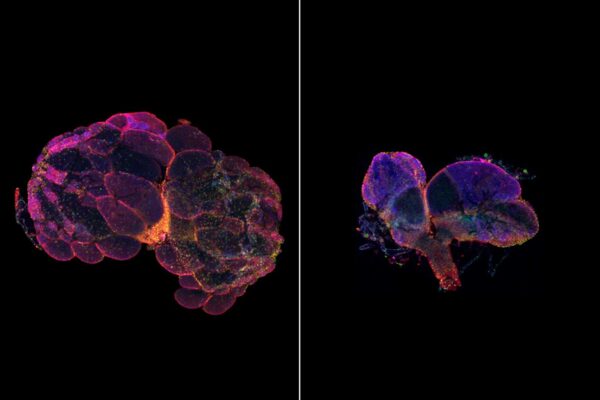
Nasal vaccine against COVID-19 prevents infection in mice
Washington University School of Medicine scientists have developed a vaccine that targets the SARS-CoV-2 virus, can be given in one dose via the nose and is effective in preventing infection in mice susceptible to the novel coronavirus.
Drug development for severe respiratory diseases supported with $3.9 million grant
School of Medicine researchers have received a $3.9 million grant supporting new technologies and therapeutics to advance a drug to treat debilitating lung diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The research is led by Michael J. Holtzman, MD.
Clinical trial focuses on reducing overactive immune response in COVID-19
School of Medicine researchers are investigating whether a drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat rare diseases of an overactive immune system could help critically ill patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
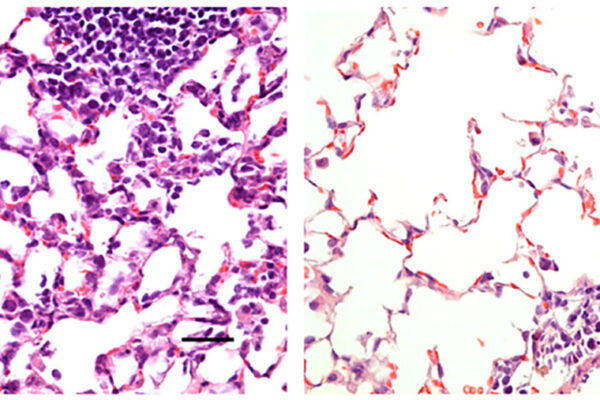
Vaccine prevents pneumonia, elicits high levels of protective antibodies
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have created a COVID-19 vaccine candidate from a replicating virus. This experimental vaccine has proven effective at preventing pneumonia in mice.
Older Stories