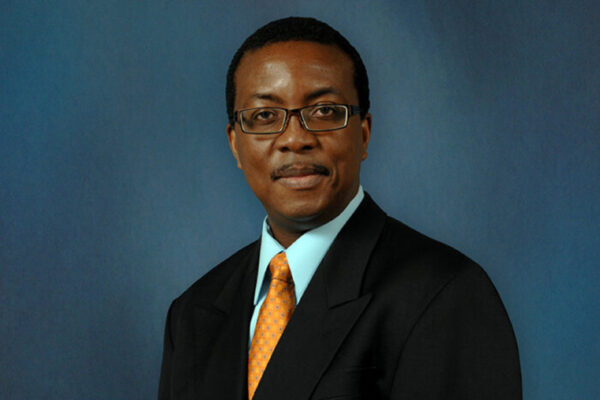
Odibo named director of maternal-fetal & ultrasound division in OB-GYN
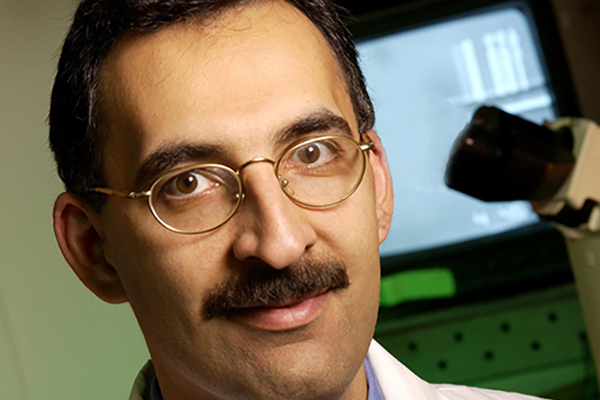
Anthony Odibo, MD, an internationally respected maternal-fetal medicine expert, has been named director of the Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine & Ultrasound in the Department of Obstetrics & Gynecology at the School of Medicine.
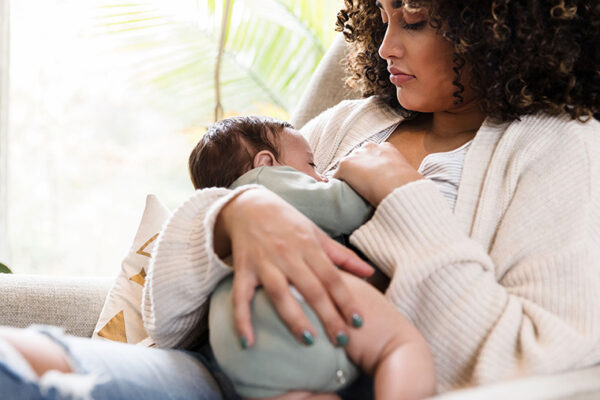
For breastfeeding moms, COVID-19 vaccinations may also protect babies
New research from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may also protect their babies from the virus.
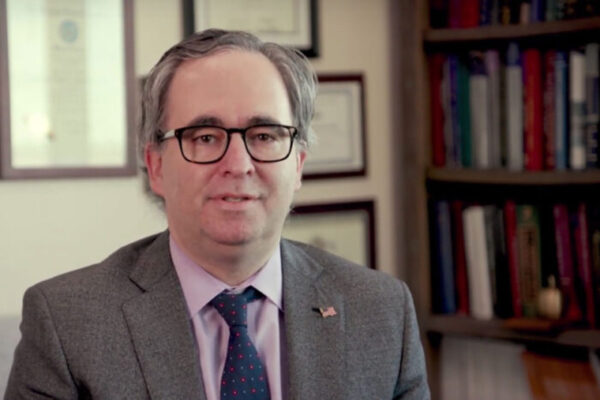
Sacks named division director in plastic and reconstructive surgery
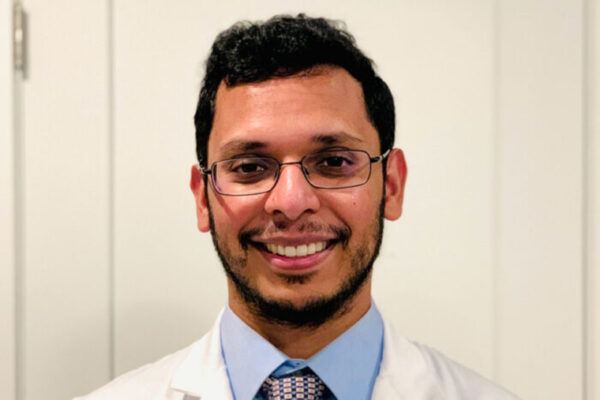
Justin M. Sacks, MD, a highly respected microvascular surgeon with expertise in complex surgeries involving cancer and trauma, has been named director of the Division of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery at the School of Medicine. Sacks also has been installed as the Sydney M. Shoenberg Jr. and Robert H. Shoenberg Endowed Chair in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, an endowment supported through The Foundation for Barnes-Jewish Hospital.
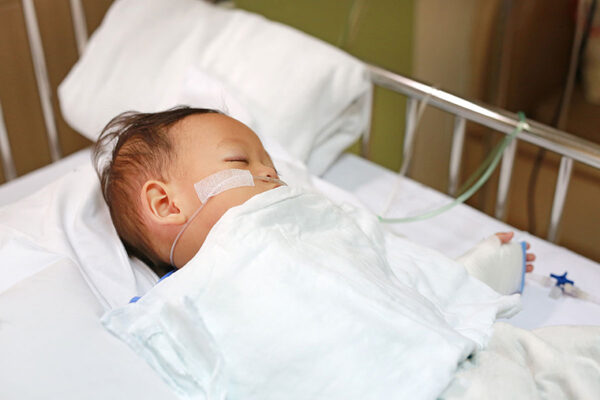
Study predicts which kids hospitalized with RSV likely to worsen
Children hospitalized with breathing problems due to infection with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are likely to get sicker and remain hospitalized if they have high levels of defective copies of the virus, according to a new study by researchers at the School of Medicine.
Holmes awarded HHMI fellowship for promising early-career scientists
Virologist Autumn Holmes, a postdoctoral researcher at the School of Medicine, has been named a Hanna H. Gray Fellow by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI). The fellowship provides up to $1.4 million over eight years to outstanding early-career scientists.
Scientists find genetic link to clogged arteries
A new study from the School of Medicine has identified a gene — called SVEP1 — that makes a protein that influences the risk of coronary artery disease independent of cholesterol.
Guilak recognized for research in cartilage engineering
Farshid Guilak, the Mildred B. Simon Research Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery and co-director of the Washington University Center of Regenerative Medicine, has received the 2021 Elizabeth Winston Lanier Kappa Delta Award for his research involving the treatment of arthritic joints.
Medical student receives fellowship to study skin microbiome, diseases
Faisal Ahmad, a second-year medical student at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, is one of 55 recipients of a $5,000 summer research fellowship from the Alpha Omega Alpha National Honor Medical Society.
Big Ideas program seeks applications
The Big Ideas 2021-2022 competition is open. The program provides opportunities for collaborative teams to develop innovations in informatics and health-care delivery The deadline to submit a letter of intent is March 29.
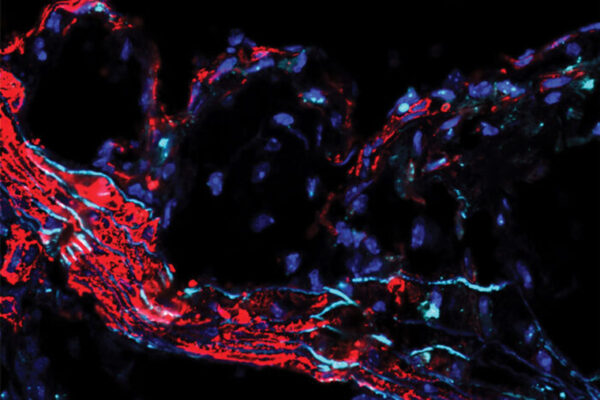
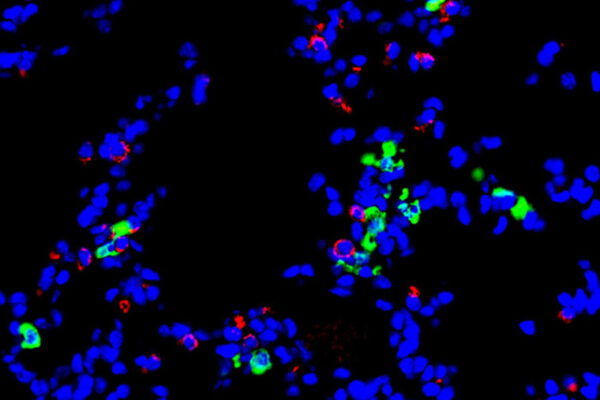
Immune cell implicated in development of lung disease following viral infection
Scientists at the School of Medicine have implicated a type of immune cell in the development of chronic lung disease that sometimes is triggered following a respiratory viral infection. The study was published in The Journal of Immunology.
Older Stories