‘First-in-class’ tool for potential treatment of brain disorders
Biomedical engineer Hong Chen at the McKelvey School of Engineering will use a $2.1 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to find noninvasive tools to treat the brain.
$7 million to support research into how human genome works
Washington University School of Medicine will serve as the data and administrative coordinating center for a national effort to investigate how variations in the human genome sequence affect how the genome functions. Such information is critical for understanding human health and diseases.
Researcher wins NIH grant
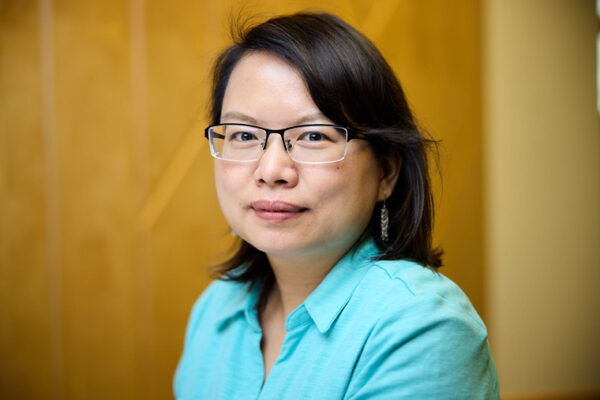
Janice L. Robertson, assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biophysics at the School of Medicine, received a four-year $1.39 million renewal grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for her research titled “Driving forces of membrane protein assembly in membranes.”
Rheumatoid arthritis treated with implanted cells that release drug
With a goal of developing rheumatoid arthritis therapies with minimal side effects, School of Medicine researchers have genetically engineered cells that, when implanted in mice, will deliver a biologic drug in response to inflammation.
Researcher wins NIH grant
Bo Zhang, at the School of Medicine, received a five-year $1.89 million Maximizing Investigators’ Research Award from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) for a research project involving the human genome.
Distilling 70 years’ worth of data
Research from the lab of Jonathan Silva at the McKelvey School of Engineering leveraged computational models to analyze 70 years of arrhythmia-related data.
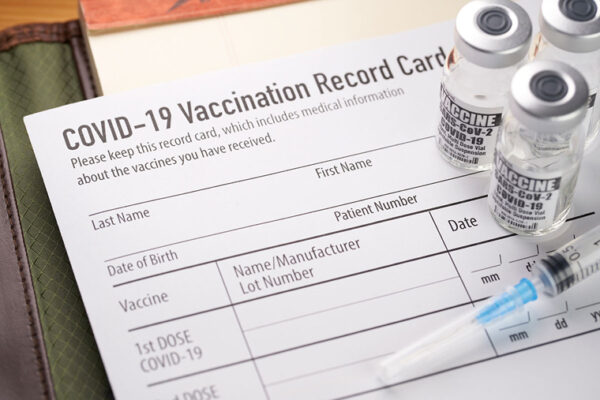
COVID-19 vaccine elicits antibodies in 90% taking immunosuppressants
Nearly 90% of people taking immunosuppressants to treat autoimmune conditions produce an antibody response to COVID-19 vaccination, but the response is weaker than those generated by healthy people, according to a study by researchers at Washington University School of Medicine.
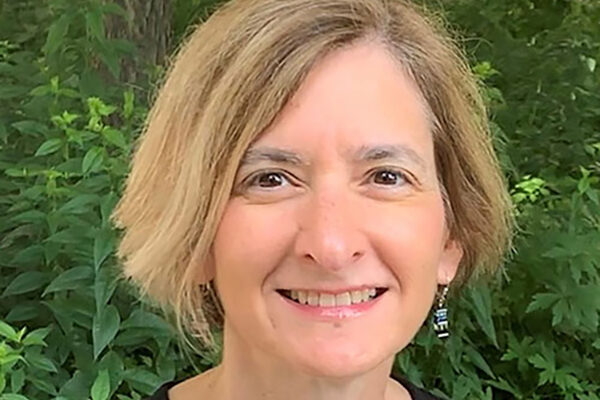
Veis named editor-in-chief of musculoskeletal research journal
Deborah Veis, MD, PhD, professor of medicine in the Division of Bone and Mineral Diseases at the School of Medicine, has been appointed the next editor-in-chief of the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research Plus. Her five-year term begins Sept. 1.
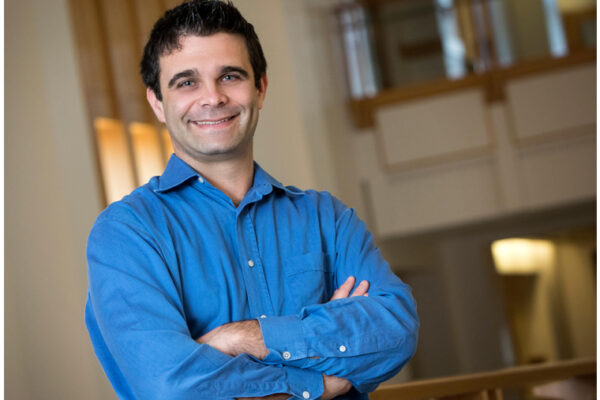
NIH awards nearly $2M to Huebsch for study
The McKelvey School of Engineering’s Nathaniel Huebsch will use a nearly $2 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, the most common cause of sudden death in young people.
Oxygen-delivering hydrogel accelerates diabetic wound healing
A new, drug-free technology developed in the lab of Jianjun Guan at the McKelvey School of Engineering helps speed up the healing process of diabetic wounds.
Older Stories