Patients want AI, doctors to work together
Interdisciplinary Washington University research finds patients may be OK with artificial intelligence playing a role in medical diagnostics.
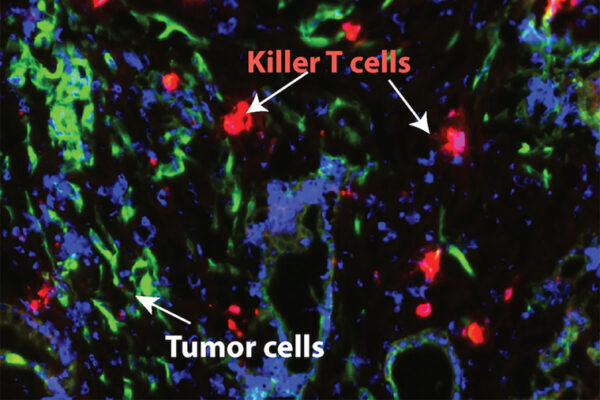
Novel treatment makes pancreatic cancer susceptible to immunotherapy, mouse study shows
New research from Washington University School of Medicine shows that blocking a major inflammatory pathway in pancreatic cancer makes the tumors sensitive to chemotherapy and a type of immunotherapy that helps the immune system’s T cells to attack cancer cells.
Low-cost, 3D printed device may broaden focused ultrasound use
WashU’s Hong Chen and her team have developed a method for producing a low-cost, easy-to-use focused ultrasound device that can help open up the blood-brain barrier for non-invasive procedures and diagnostics.
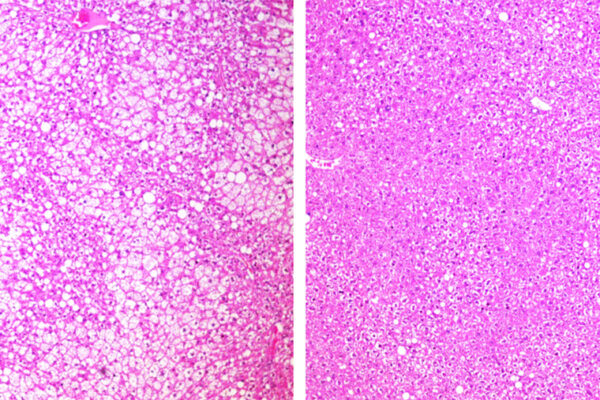
Drug mimics beneficial effects of fasting in mice
An investigational cancer drug that starves tumors of their energy supply also shows evidence of improving whole body metabolism, according to a new study in mice from Washington University School of Medicine.
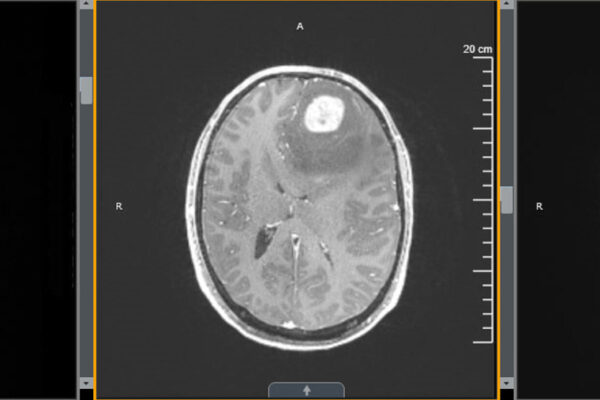
Boosting T cells improves survival in mice with glioblastoma
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine shows that treatment with an immune-boosting protein called interleukin 7 (IL-7) in combination with radiation improves survival in mice with glioblastoma.
Cancer Navigation
Charting the Path Forward for Low Income Women of Color
Cancer Navigation: Charting the Path Forward for Low Income Women of Color is a practical quick-reference resource for U.S. health care providers working with marginalized women throughout the cancer continuum.
New treatment target ID’d for radiation-resistant cervical cancer
Two new studies from Washington University School of Medicine have identified a previously unrecognized pathway of cell death — named lysoptosis — and demonstrate how it could lead to new therapies for cervical cancer.
For children, young adults with recurrent AML, immunotherapy shows promise
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have shown, in a small clinical trial, that pre-activated natural killer cells can help some children and young adults with recurrent acute myeloid leukemia and few other treatment options.
Asthma may reduce risk of brain tumors — but how?
Asthma has been associated with a lowered risk of brain tumors, and researchers at Washington University School of Medicine now think they know why: Immune cells activated under conditions of asthma are less able to promote the growth of brain tumors.
Antipsychotic drugs may increase risk of breast cancer
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine have found that many commonly prescribed antipsychotic medications are associated with a significant increase in risk of breast cancer.
Older Stories