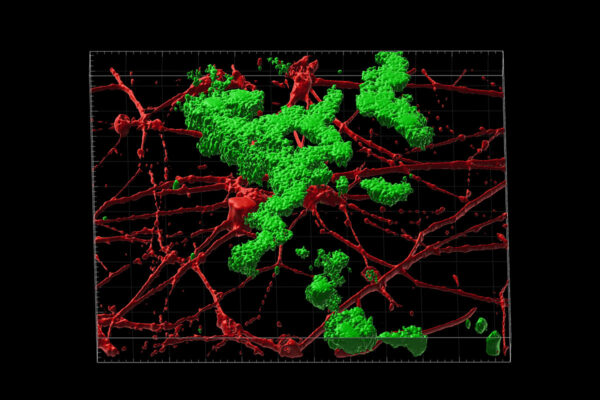
Electrochemical field key to how dementia precursors ‘break bad’
Researchers at Washington University have found electrochemical rules for how toxic protein assemblies form, opening the way for better treatments of dementia.
Next-gen Alzheimer’s drugs extend independent living by months
An analysis by researchers at WashU Medicine interprets the benefits of new Alzheimer’s drugs in a way that aims to help patients and families make informed treatment decisions.
Scientists race to decode how this man defied his Alzheimer’s destiny
A Washington man who inherited a mutation that should have caused him to develop Alzheimer’s decades ago remains mentally sharp. A new study of his case by researchers at WashU Medicine aims to identify potential routes to preventing or treating the disease.
International Alzheimer’s prevention trial in young adults begins
The first participants have been enrolled in an international clinical trial, led by WashU Medicine, aimed at preventing Alzheimer’s disease in young adults at high risk of the disease.
Grant will fund development of vaccines to prevent dementia
Researchers at Washington University are looking to find new ways to design vaccines to protect against inflammation in the brain that causes dementia.
New drug targets for Alzheimer’s identified from cerebrospinal fluid
Researchers at WashU Medicine have linked disease-related proteins and genes to identify specific cellular pathways responsible for Alzheimer’s genesis and progression.
Healthy brains suppress inappropriate immune responses
Researchers at WashU Medicine have found a process in which the brain guards against attack by the immune system, opening opportunities to pursue new therapies for diseases such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s.
Zhao, Musiek receive NIH grant to study neurodegenerative diseases
Guoyan Zhao, PhD, and Erik Musiek, MD, PhD, both at WashU Medicine, have received a $433,000 grant from the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to study brain cells called astrocytes and their roles in neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Multiple sclerosis appears to protect against Alzheimer’s disease
WashU Medicine experts in Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis (MS) find that MS patients are less likely to have amyloid plaques than adults without MS.
Aging-related genomic culprit found in Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a way to study aged neurons in the lab without a brain biopsy, allowing them to accurately model the effects of aging in the development of late-onset Alzheimer’s disease.
Older Stories