Achilefu, Elgin to receive 2018 faculty achievement awards
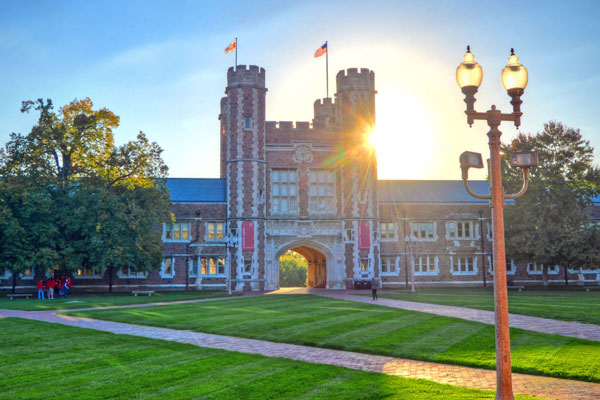
Sarah C.R. Elgin and Samuel I. Achilefu will receive Washington University in St. Louis’ 2018 faculty achievement awards, Chancellor Mark S. Wrighton announced. Also, William A. Frazier III, professor emeritus, will be honored for innovation and entrepreneurship.
Faculty, students participate in climate summit April 22-24
Washington University faculty and students will moderate panels at the Saint Louis Climate Summit, hosted by Saint Louis University. Students, faculty and staff can attend an evening with Bill Nye of “Science Guy” fame and environmentalist Carl Pope on April 23 for free by showing their IDs at the ticket booth.
Arvidson to receive Weidenbaum Center Award for Excellence
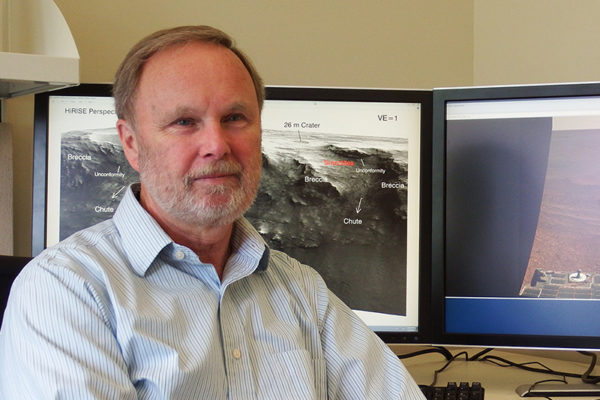
Raymond E. Arvidson, the James S. McDonnell Distinguished University Professor in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, will receive the Weidenbaum Center Award for Excellence Medal. The award will be given at a ceremony held during the Weidenbaum Center on the Economy, Government, and Public Policy annual dinner April 2. This award honors individuals who have made major contributions to both scholarship and public service.
Sadtler wins NSF CAREER award to develop better catalysts for alternative fuels
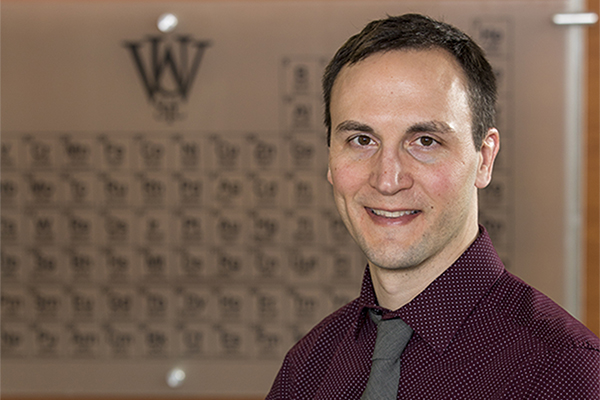
Bryce Sadtler, assistant professor of chemistry in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, has been awarded a prestigious Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) Award by the National Science Foundation. His grant, expected to total more than $610,000 over the next five years, is for research to identify the structural characteristics that make some catalysts better than others for harvesting energy from the sun.
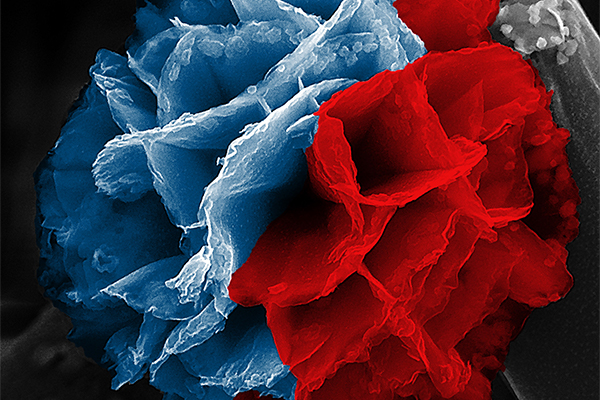
Making rusty polymers for energy storage
Research from the Department of Chemistry in Arts & Sciences advances the understanding of the chemical mechanisms involved with depositing rust and forming polymers, which will allow scientists to more easily manipulate and engineer the structures of the materials they make.
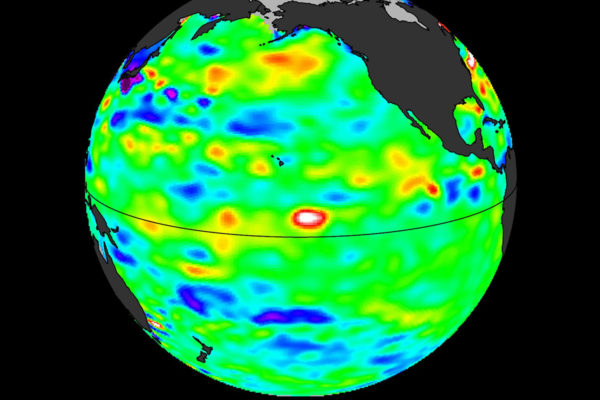
Global warming focus of 2018 McDonnell lecture
S. George Philander, one of the world’s leading experts on climate and the interactions between the ocean and atmosphere, will deliver two talks March 28 and 29 as part of the McDonnell Distinguished Lecture Series, sponsored by Washington University in St. Louis’ McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences.
Keeping plant-cell motors on track
In a growing plant cell, motor proteins called kinesins work as transporters that haul materials built in one part of the cell to the place where they are needed. Now, biologists at Washington University in St. Louis have discovered the molecular brakeman that holds kinesins in check until their cargo is needed.
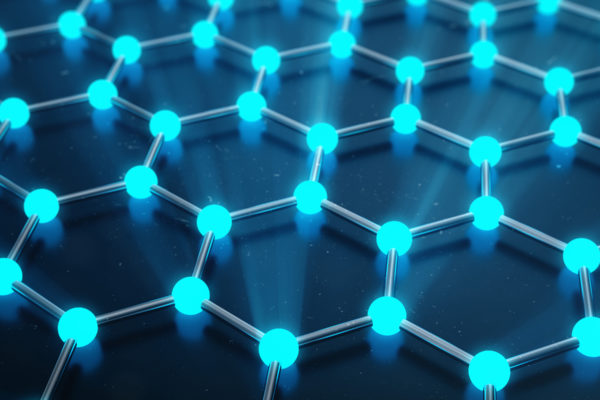
A new view on electron interactions in graphene
There’s a new way to look at how electrons interact with each other in graphene, an intriguing material comprised of a single layer of carbon atoms. Washington University in St. Louis researchers, led by Erik Henriksen, assistant professor of physics in Arts & Sciences, are exploring the quantum electronic properties of graphene using infrared light.
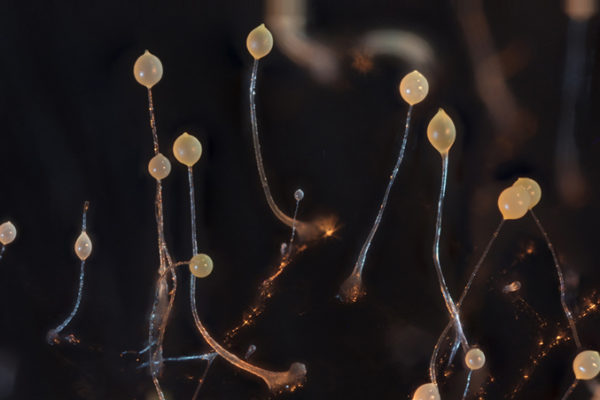
Arms races and cooperation among amoebae in the wild
Using new gene sequencing techniques, Washington University biologists are taking a closer look at the behavior of the social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum, or Dicty for short.
Haswell elected council delegate for AAAS
Elizabeth S. Haswell, associate professor of biology in Arts & Sciences, has been elected as a council delegate for biological sciences for the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Her term began Feb. 20.
View More Stories