Genes linked to Alzheimer’s contribute to damage in different ways
School of Medicine researchers have found that the pathways through which various types of brain cells are damaged by Alzheimer’s disease varies, depending on the genes involved. The findings are published in the journal Genome Medicine.
Scientists ID source of damaging inflammation after heart attack
Scientists from the School of Medicine have zeroed in on a culprit that spurs damaging inflammation in the heart following a heart attack. The guilty party is a type of immune cell that tries to heal the injured heart but instead triggers inflammation that leads to even more damage.
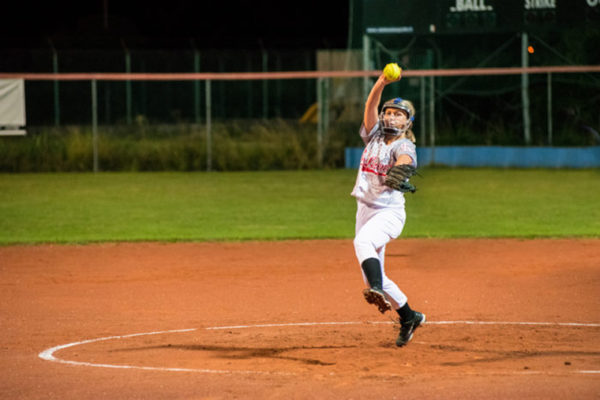
Are fast-pitch softball pitchers overdoing it?
Youth baseball leagues often have fairly strict limits on how many innings pitchers can pitch or how many pitches a player can throw. But for girls playing fast-pitch softball, such guidelines are rare. School of Medicine sports medicine specialists have found that many pitchers aren’t getting enough time to recover and are experiencing shoulder fatigue, pain, weakness and injury.
Smoking rates decline when mentally ill get help to quit
Recognition of a disconnect between what patients with serious mental illness want and what health providers think they want appears to be a crucial step in reducing smoking rates among such patients, School of Medicine researchers found.
Drugs that suppress immune system may protect against Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s disease is caused by the injury or death of brain cells known as dopaminergic neurons. A new School of Medicine study shows that people who take drugs that suppress the immune system are less likely to develop the disease, which is characterized by difficulty with movement.
Brain cancer vaccine effective in some patients
Most people with the deadly brain cancer glioblastoma die less than 18 months after diagnosis. But a multicenter clinical trial of a personalized vaccine that targets the aggressive cancer has indicated improved survival rates for such patients. The study appears May 29 in the Journal of Translational Medicine.
Eczema drug effective against severe asthma
Two new studies of patients with difficult-to-control asthma show that the eczema drug dupilumab alleviates asthma symptoms and improves patients’ ability to breathe better than standard therapies. Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues elsewhere conducted the studies.
Clues found to early lung transplant failure
Researchers at the School of Medicine and colleagues at Northwestern University and elsewhere have uncovered new clues in early lung transplant failure.
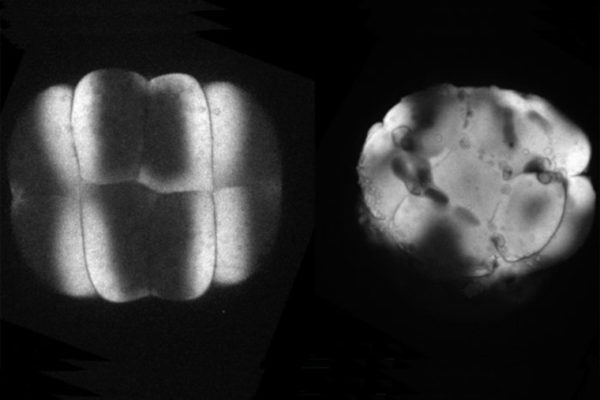
Revealing the mysteries of early development
Zebrafish embryos are transparent and develop outside the mother’s body, giving scientists a detailed view of early development. A research team led by Lila Solnica-Krezel, of the School of Medicine, is revealing new clues to how birth defects develop.
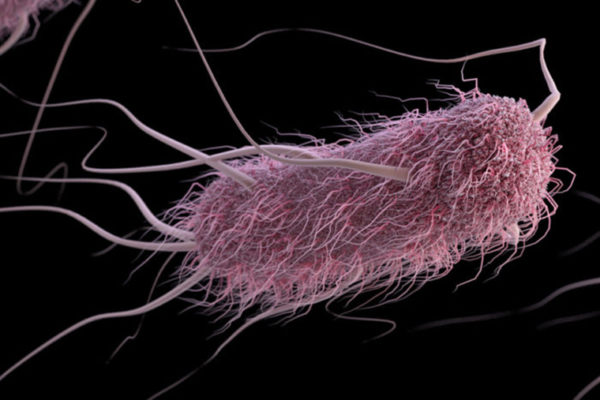
Blood type affects severity of diarrhea caused by E. coli
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that a kind of E. coli most associated with “travelers’ diarrhea” and children in underdeveloped areas of the world causes more severe disease in people with blood type A. The findings could lead to a vaccine that could potentially protect people with type A blood against the deadliest effects.
View More Stories