Brain network connections may underlie social behavior linked to autism
Researchers at School of Medicine, with colleagues from the multicenter Infant Brain Imaging Study (IBIS) network, have found associations between brain connectivity and a key social behavior that is a central feature of autism.
NICU study highlights importance of sound
Premature babies often spend the first several weeks of life in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), where, ideally, they are protected from too much noise stimulation. However, researchers at the School of Medicine have found that preemies may be exposed to noise levels higher than those deemed safe by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Effort to improve radiation therapy for veterans receives nearly $4 million
In a national effort to improve and standardize radiation therapy for U.S. veterans with cancer, the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) has contracted with Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis for an additional $3.8 million to fund the project.
Drug combination effective against chikungunya arthritis in mice
Combining a drug for rheumatoid arthritis with one that targets the chikungunya virus can eliminate the signs of chikungunya arthritis in mice in the disease’s earliest stage, according to researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
$4 million funds study of sickle cell disease in teens, adults
Allison A. King, MD, PhD, a highly regarded sickle cell disease researcher at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has received a six-year, $4.3 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to further her investigations into the disease.
Early signs of anxiety, depression may be evident in newborns
Early predictors of anxiety and depression may be evident in the brain even at birth, suggests a study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Online database aims to collect, organize research on cancer mutations
Researchers at the School of Medicine have developed an online “knowledgebase” intended for the gathering and organization of the vast body of knowledge known as cancer genomics.
Drug compound halts Alzheimer’s-related damage in mice
Researchers at the School of Medicine have shown that levels of tau protein can be reduced – and some of the neurological damage caused by tau even reversed – by a synthetic molecule that targets genetic instructions. The findings are important for Alzheimer’s and other neurological diseases.
Study unveils new way to starve tumors to death
School of Medicine scientists have exploited a common weak point in cancer cell metabolism, forcing tumor cells to reveal the backup fuel supply routes they rely on when this weak point is compromised. Mapping these secondary routes, the researchers also identified drugs that block them.
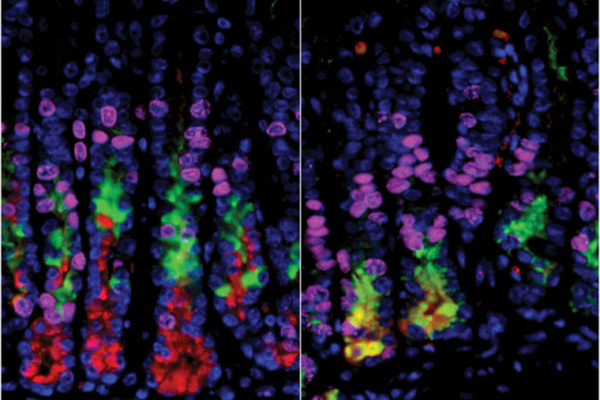
New insight into origin of stomach cancer
New research at the School of Medicine and Siteman Cancer Center have found that damage to acid-secreting cells alone doesn’t jump-start the transformation of healthy cells into precancerous cells — at least in a mouse model.
View More Stories