Scientists get closer look at living nerve synapses
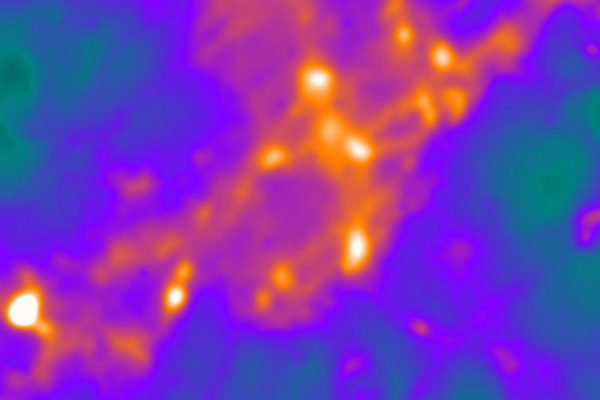
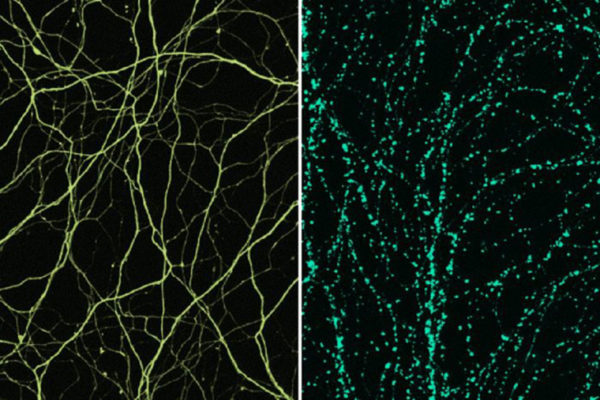
The brain hosts an extraordinarily complex network of interconnected nerve cells that are constantly exchanging electrical and chemical signals at speeds difficult to comprehend. Now, scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report they have been able to achieve — with a custom-built microscope — the closest view yet of living nerve synapses.
Surprising culprit in nerve cell damage identified
Scientists at the School of Medicine have implicated a specific molecule in the self-destruction of axons, the wiring of the nervous system. Understanding just how that damage occurs may help researchers find a way to halt it.
Spinal cord stimulation relieves back pain without opioids
Doctors who treat back pain are exploring new approaches that help some patients avoid opioid drugs. One option available at the Washington University Pain Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital involves stimulating the spinal cord with very short pulses of electricity.
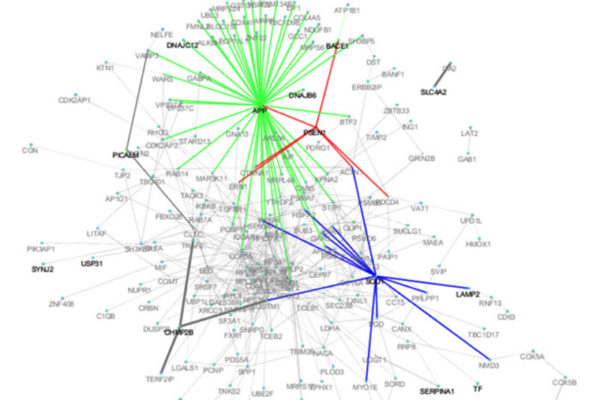
$7 million aimed at illuminating the genetics of Alzheimer’s disease
Two new studies led by the School of Medicine aim to clarify the genetic underpinnings of Alzheimer’s disease. Funded by grants totaling $7 million from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), researchers seek to find ways to predict who will develop the disease as well as new targets for therapies.
Brain hardwired to respond to others’ itching
Washington University School of Medicine researchers have found that socially contagious itching is hardwired in the brain. Studying mice, the scientists identified what happens in the brain when a mouse feels itchy after seeing another scratch.
New weight-loss therapy rids body of food before digestion
A new weight-loss therapy offers significantly overweight people a means to rid their bodies of some of what they eat before excess calories can be absorbed. Called aspiration therapy, the FDA-approved, nonsurgical therapy was developed by researchers at the School of Medicine and is available at Barnes-Jewish West County Hospital.
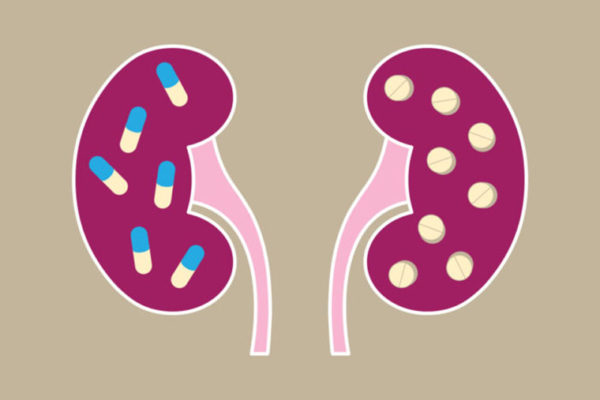
Popular heartburn drugs linked to gradual yet ‘silent’ kidney damage
Taking popular heartburn medication for prolonged periods may lead to serious kidney damage, even in people who show no signs of kidney problems, according to researchers at the School of Medicine and the Veterans Affairs St. Louis Health Care System.
Study reveals ways to improve outcomes, reduce costs for angioplasty
Hospitals can improve patient care and reduce costs associated with coronary angioplasty if cardiologists perform more procedures through an artery in the wrist and if they discharge patients on the same day, finds a new study led by the School of Medicine.
New collaboration with Pfizer aimed at speeding drug discovery
Washington University in St. Louis is collaborating with the biopharmaceutical company Pfizer Inc. on research aimed at speeding the development of new drugs. The university is the first academic institution in the Midwest to join Pfizer’s Centers for Therapeutic Innovation’s (CTI) collaborative network.
New guidance developed for children hospitalized with mild head trauma
In new research, pediatric neurosurgeons at the School of Medicine developed a risk scoring system intended to help determine whether a child with mild traumatic brain injury and an abnormal CT scan can be monitored safely in a general hospital ward or requires the increased surveillance of an intensive care unit (ICU).
View More Stories