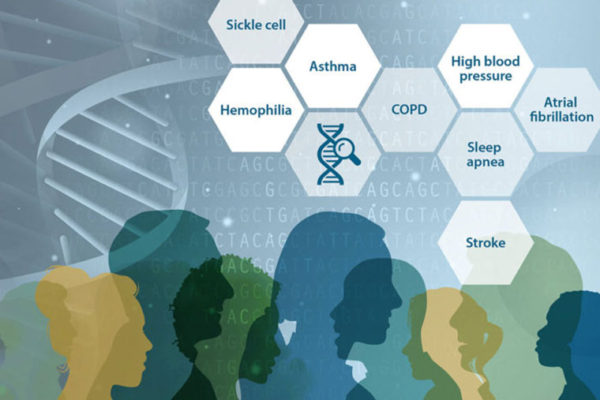
$10 million DNA sequencing effort aims to shed light on lung diseases
Washington University’s McDonnell Genome Institute has received $10 million from the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute (NHLBI) to sequence the DNA of people from diverse ethnic backgrounds, in an effort to identify the genetic roots of COPD and other lung disorders.
UTI treatment reduces E. coli, may offer alternative to antibiotics
A new study from the School of Medicine has found that a molecular decoy can target and reduce UTI-causing bacteria in the gut. With a smaller pool of disease-causing bacteria, the researchers say the risk of having a UTI goes down.
Makeup of vaginal microbiome linked to preterm birth
In a study of predominantly African-American women — who have a much higher rate of delivering babies early compared with other racial groups — researchers at the School of Medicine showed that a decrease in the diversity of vaginal microbes of pregnant women between the first and second trimesters is associated with preterm birth.
$10 million gift to benefit Center for Genome Sciences
The School of Medicine has received a $10 million gift from the Harry Edison Foundation to support the Center for Genome Sciences and Systems Biology. The gift will help to advance the center’s innovative research programs, including its substantial work in understanding the gut microbiome.
Type of sugar may treat atherosclerosis, mouse study shows
Researchers from the School of Medicine have found that the immune system may be triggered to treat atherosclerosis and possibly other metabolic conditions, including fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes.
Study urges aggressive treatment for sepsis
Tiffany M. Osborn, MD, professor of surgery and of emergency medicine at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis is a leading expert in sepsis. She co-authored a study published May 21 in The New England Journal of Medicine that stresses the need for an aggressive response to the condition.
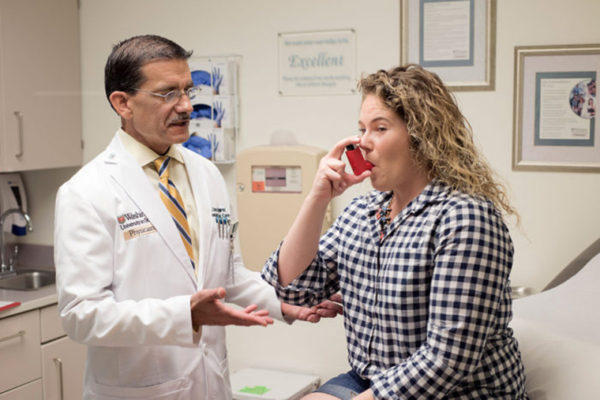
Cancer drug may help patients with severe asthma
A small clinical trial conducted in part at the School of Medicine suggests that some patients with severe asthma may benefit from a drug commonly prescribed to treat chronic myeloid leukemia.
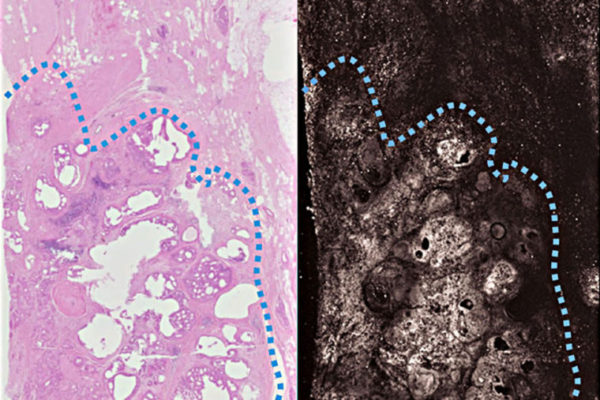
New imaging technique aims to ensure surgeons completely remove cancer
Researchers at the School of Medicine in St. Louis and California Institute of Technology have developed a technology to scan a breast tumor sample and produce images detailed enough to check whether a tumor has been completely removed.
Antibiotic resistance circumvented in lab
As dangerous bacteria grow more savvy at evading antibiotics, researchers are seeking new ways to counterattack. Rather than design new drugs from scratch, some scientists are searching for ways to block the microbes’ evasive maneuvers. If resistance can be shut down, current drugs should remain effective. That concept is demonstrated in a new study from the School of Medicine.
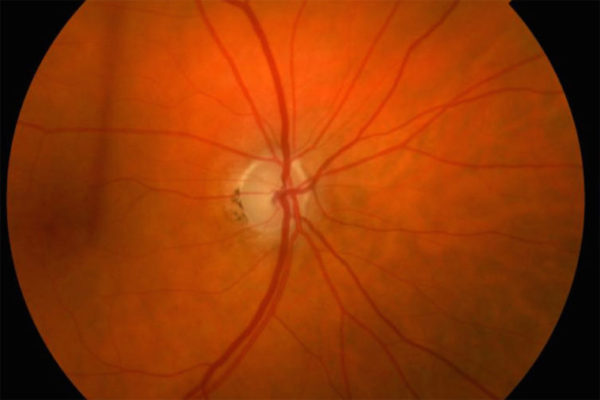
Potential predictor of glaucoma damage identified
Researchers at the School of Medicine have identified a marker of damage to cells in the eye that potentially could be used to monitor progression of glaucoma and the effectiveness of treatment.
View More Stories