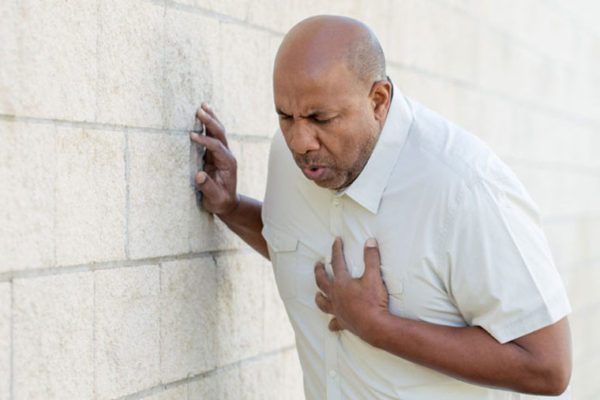
Aggressive testing provides no benefit to patients in ER with chest pain
Ten million people come to the ER with chest pain each year in the United States. A new School of Medicine study shows that these patients are getting more testing than is necessary to rule out heart attacks and that such patients do not need CT scans or cardiac stress tests, according to the researchers.
Can laughing gas help deter suicide?
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis are studying nitrous oxide as a possible treatment for patients who are hospitalized due to suicidal thoughts.
How cells detect, mend DNA damage may improve chemotherapy
Human cells have a way of detecting and mending DNA damage caused by some common chemotherapy drugs, according to a new study from the School of Medicine. The findings could have important implications for treating cancer.
In autism, too many brain connections may be at root of condition
A defective gene linked to autism influences how neurons connect and communicate with each other in the brain, according to a study from the School of Medicine. Rodents that lack the gene form too many connections between brain neurons and have difficulty learning.
Penny-wise, pound-foolish decisions explained by neurons’ firing
A new study at the School of Medicine suggests that being penny wise and pound foolish is not so much a failure of judgment as it is a function of how our brains tally the value of objects that vary widely in worth.
Early childhood adversities linked to health problems in tweens, teens
School of Medicine researchers have identified a pathway in the brain that seems to connect exposure to adverse experiences during early childhood with depression and problems with physical health in teens and preteens.
Key malaria parasite findings could lead to new treatments
Researchers at the School of Medicine have identified how the malaria parasite gets into and out of red blood cells, and chemical compounds that block the process. The findings could lead to desperately needed new drugs for the deadly mosquito-borne disease.
Large declines seen in teen substance abuse, delinquency
More than a decade of data indicates teens have become far less likely to abuse alcohol, nicotine and illicit drugs, and they also are less likely to engage in delinquent behaviors, such as fighting and stealing, according to results of a national survey analyzed by researchers at the School of Medicine.
New gene-altering treatment offered for certain blood cancers
A new immunotherapy that targets certain blood cancers is being offered for the first time at Siteman Cancer Center. Newly approved by the FDA for types of advanced non-Hodgkin lymphoma in adults, the CAR-T cell therapy harnesses a patient’s own immune system to fight cancer.
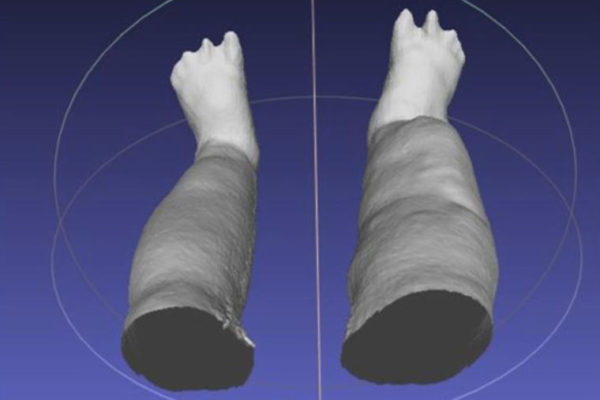
Portable 3-D scanner assesses patients with elephantiasis
Scientists at the School of Medicine in St. Louis, working with collaborators in Sri Lanka, have shown that a portable scanning device can measure limb enlargement and disfigurement faster and more easily in patients with elephantiasis.
View More Stories