Fighting the vaccine wars on the side of science
Michael Kinch’s new book, “Between Hope and Fear: A History of Vaccines and Human Immunity,” tells the story of the people behind vaccines and how the human body fights infection.
Overlooked signal in MRI scans reflects amount, kind of brain cells
An MRI scan often generates an ocean of data, most of which is never used. When overlooked data is analyzed using a new technique developed at the School of Medicine, they surprisingly reveal how many and which brain cells are present – and show where cells have been lost through injury or disease. The findings could lead to new treatments for a variety of brain diseases.
Washington University joins network for solving rare medical mysteries
The School of Medicine is joining a national research network aimed at diagnosing rare, previously undescribed diseases in patients whose conditions present as medical mysteries. The Undiagnosed Diseases Network is funded by the NIH and made up of 12 clinical sites and several research centers across the country.
Why some TB bacteria prove deadly
Researchers at the School of Medicine have found that the same mutation that gives tuberculosis bacteria drug resistance also elicits a weaker immune response. The findings are published in Nature Microbiology.
Genetic testing helps predict disease recurrence in myelodysplastic syndrome
A DNA-based analysis of blood cells soon after a stem cell transplant can predict likelihood of disease recurrence in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), a group of cancerous disorders characterized by dysfunctional blood cells, according to new research at the School of Medicine.
Gordon receives Luminary Award
The School of Medicine’s Jeffrey I. Gordon, MD, has received a 2018 Luminary Award from the Precision Medicine World Conference. He is being honored for his pioneering work in founding the field of gut microbiome research and for fundamentally altering the understanding of the origins of human health and disease, especially as they relate to nutrition.
Scientists identify weak point in deadly eye melanoma
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that — in human tumor cells grown in the lab — a natural plant compound shuts down uveal melanoma cell growth.
New clues found to understanding relapse in breast cancer
A new study by the School of Medicine and others identifies mutations associated with relapse in ER positive breast cancer — knowledge that could lead to better therapies.
Experimental drug shows promise as multiple sclerosis treatment
An experimental drug reduces brain atrophy in people with progressive multiple sclerosis, raising hopes that it also can reduce disability. The School of Medicine is one of 28 clinical sites participating in the study.
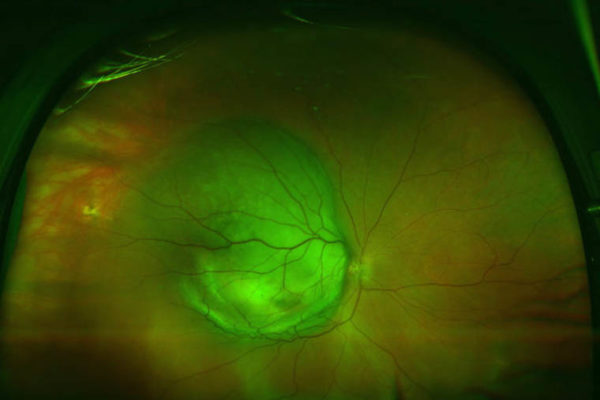
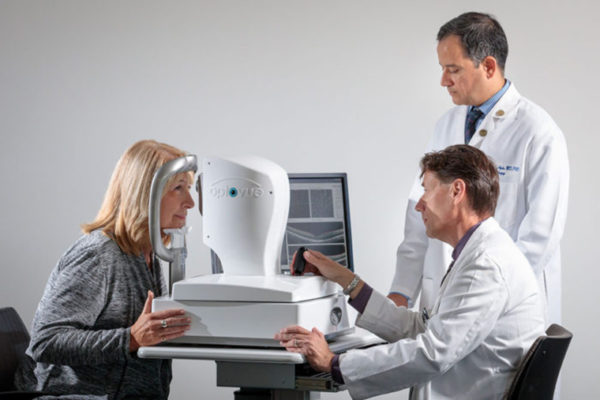
Alzheimer’s one day may be predicted during eye exam
Using technology similar to what is found in many eye doctors’ offices, School of Medicine researchers have detected evidence suggesting Alzheimer’s in older patients who had no symptoms of the disease.
View More Stories