Gut microbes linked to deadly intestinal disease in preemies
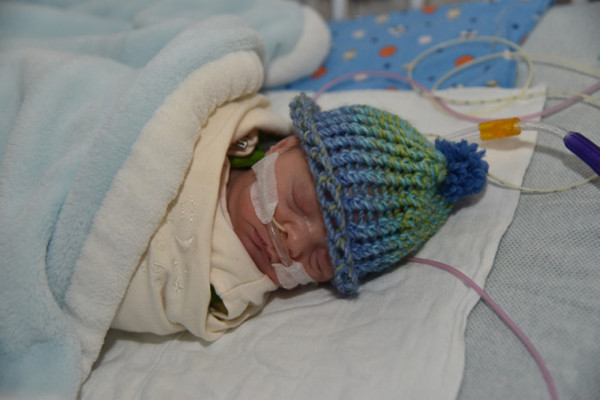
An imbalance of certain gut microbes appears to be the underlying cause of a frequently fatal intestinal illness in premature babies, according to new research led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Shedding light on the day-night cycle
New research sheds light on how the rhythms of daily life are encoded in the brain. Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have discovered that different groups of neurons, those charged with keeping time, become active at different times of day despite being on the same molecular clock.
Treating students where they are
The Jennings School District, in partnership with Washington University School of Medicine, has launched a free, on-site health and social-services clinic called Supporting Positive Opportunities for Teens — The SPOT at Jennings.
Laser surgery opens blood-brain barrier to chemotherapy
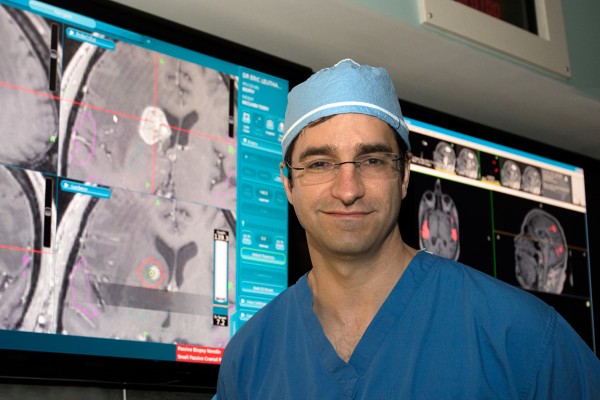
Using a laser probe, neurosurgeons at the Medicine have opened the brain’s protective cover, enabling them to deliver chemotherapy drugs to patients with a form of deadly brain cancer called glioblastoma.
Dietary link to stunted growth identified
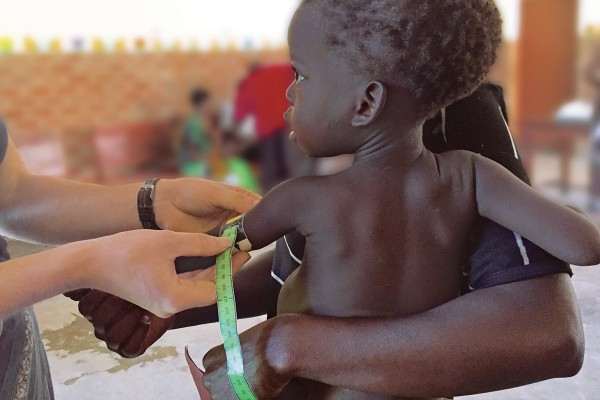
A team of researchers led by senior author Mark J. Manary, MD, at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, has found that inadequate dietary intake of essential amino acids and the nutrient choline is linked to stunting. That knowledge may unlock the door to new approaches to treat the debilitating condition.
Natural sugar may treat fatty liver disease
New research from the School of Medicine shows that a natural sugar called trehalose prevents the sugar fructose — thought to be a major contributor to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease — from entering the liver and triggers a cellular housekeeping process that cleans up excess fat buildup inside liver cells.
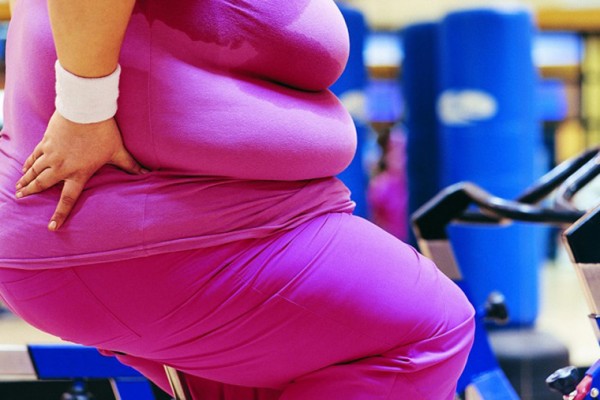
Why 5 percent weight loss can be life-changing
For patients with obesity trying to lose weight, the greatest health benefits come from losing just 5 percent of their body weight, according to a new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis.
Breakthroughs in the fight against childhood malnutrition
Two new studies led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis show that effects of gut bacteria reach far beyond the gastrointestinal tract. Manipulating the makeup of microbes in the gut has the potential to provide new ways to treat and ultimately help prevent childhood malnutrition.
What two entrepreneurs learned at an accelerator
Washington University in St. Louis alumni Andrew Hess and Philip Thomas, co-founders of a scheduling startup called Staffjoy, talk about what they learned participating in the Y Combinator Fellowship program.
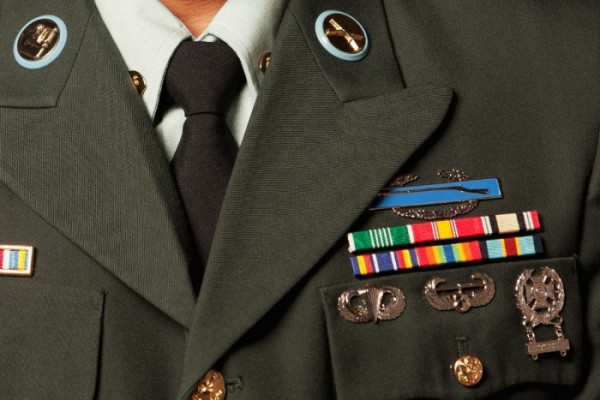
Improving veterans’ radiation therapy
Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has been selected to lead national efforts to improve and standardize radiation therapy for veterans with cancer.
View More Stories