The monster who will not leave us
Nearly 200 years after the publication of “Frankenstein” in 1818, we still employ Mary Shelley’s dream vision to interpret and explain our world today — but why? Perhaps because the troubling dialectic between Creator and Monster reflects some basic anxiety that has still not been resolved. Henry Schvey writes an essay in advance of the Oct. 13 conference “Frankenstein at 200” in Umrath Hall on the Danforth Campus.
‘Frankenstein’ for the Assembly Series
On Sept. 7, the Assembly Series’ first fall program welcomed British playwright Nick Dear Nick Dear, author of the National Theatre of Great Britain’s 2011 production of “Frankenstein” to Graham Chapel. See photos of the event here.
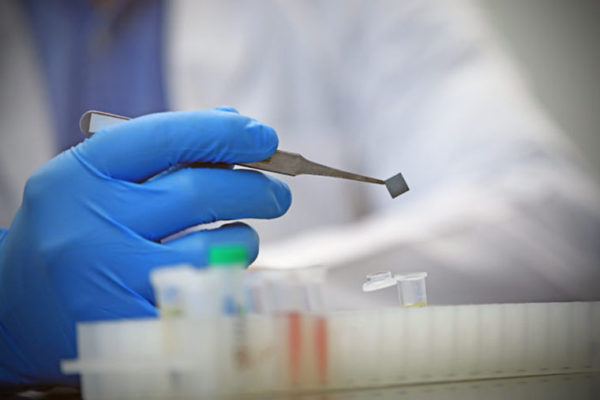
Test uses nanotechnology to quickly diagnose Zika virus
Washington University in St. Louis researchers have developed a test that quickly detects the presence of Zika virus in blood.
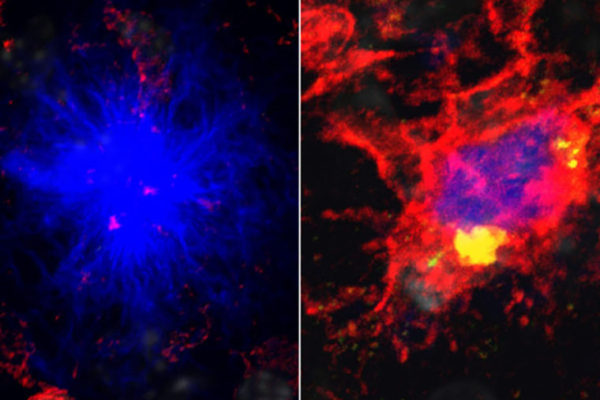
Alzheimer’s risk linked to energy shortage in brain’s immune cells
A new study from the School of Medicineshows that mutations in the gene TREM2 cause an energy shortage in the brain’s immune cells, leading to their failure to protect neurons from damaging clumps of protein.
Drug trial shows promise for deadly neurological disorder
Results of a small clinical trial show promise for treating a rare neurodegenerative condition that typically kills those afflicted before they reach age 20. The disease, called Niemann-Pick type C (NPC), causes cholesterol to build up in neurons, leading to a gradual loss of brain function.
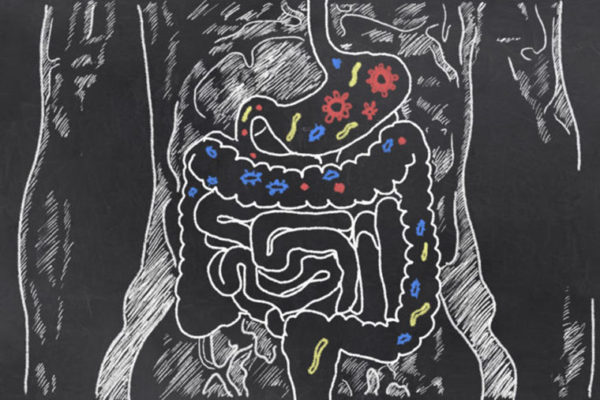
Protein-rich diet may help soothe inflamed gut
The combination of a bacterium that normally lives in the gut and a protein-rich diet promotes a more tolerant, less inflammatory gut immune system, according to new research at the School of Medicine. The findings may potentially spell relief for people living with inflammatory bowel disease.
Natural compound coupled with specific gut microbes may prevent severe flu
A new study from the School of Medicine shows that a particular gut microbe can prevent severe flu infections in mice, likely by breaking down naturally occurring compounds — called flavonoids — commonly found in foods such as black tea, red wine and blueberries.
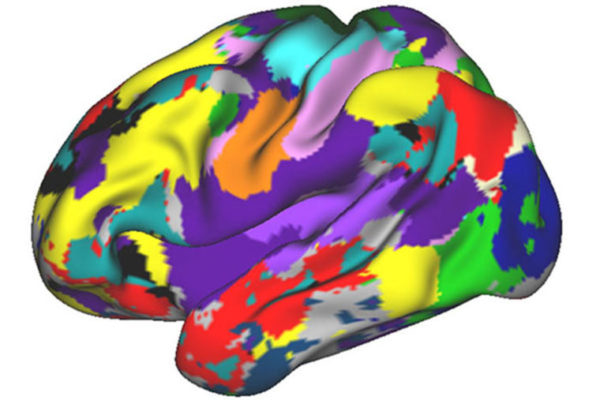
Scientists become subjects in brain-scanning project
A research group started in 2013 by two neuroscientists at the School of Medicine collected a massive amount of data on individual brains. The study’s subjects were the scientists themselves and eight others, all junior faculty or graduate students.
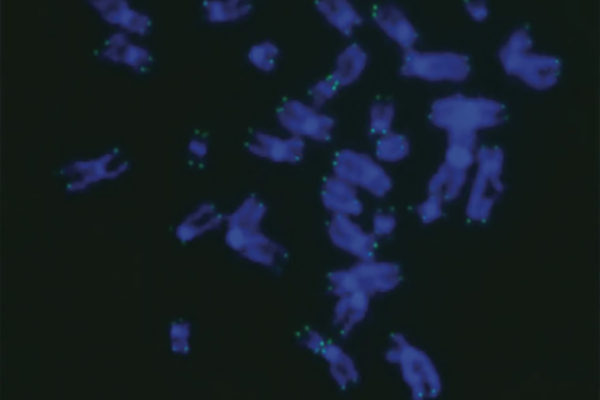
CRISPR sheds light on rare pediatric bone marrow failure syndrome
Using the gene editing technology CRISPR, scientists at the School of Medicine have shed light on a rare, sometimes fatal syndrome that causes children to gradually lose the ability to manufacture vital blood cells.
Siteman Cancer Center opens north St. Louis County location
Siteman Cancer Center will begin seeing patients July 1 at its newest satellite location, Christian Hospital in north St. Louis County. Siteman Cancer Center is based at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine, and the new location is Siteman’s fifth in the St. Louis area.
View More Stories