$6.3 million for center to develop new tracers for PET scans
With the help of a five-year, $6.3 million NIH grant, School of Medicine radiologist Robert J. Gropler, MD, aims to help PET technology reach its potential by expanding the community of PET researchers.
Scientists design way to track steps of cells’ development
Scientists at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have developed a new tool described as a “flight data recorder” for developing cells, illuminating the paths cells take as they progress from one type to another.
Rates of chronic kidney disease, deaths outpace other diseases
An abundance of high-sugar, high-salt foods in many American diets and obesity-related health problems such as diabetes are likely driving an increase in kidney disease cases, including in young adults, according to School of Medicine researchers.
$20 million gift boosts multiple myeloma research
A $20 million gift from Paula C. and Rodger O. Riney will help researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis develop new treatments for multiple myeloma.
Alcohol dependence, psychiatric disorders share genetic links
An international team of researchers, including a team from the School of Medicine, has identified a gene that regulates how quickly the body metabolizes alcohol as a key risk factor for alcohol dependence. The researchers also linked genetic factors associated with alcohol dependence to other psychiatric disorders.
Probiotics no help to young kids with stomach virus
A major U.S. study led by School of Medicine researchers has found that a commonly used probiotic is not effective in improving symptoms of diarrhea and vomiting in young children with gastroenteritis.
MRI scans shows promise in predicting dementia
Doctors may one day be able to gauge a patient’s risk of dementia with an MRI scan, according to a new study from the School of Medicine. Using a new technique for analyzing MRI data, researchers were able to predict who would experience cognitive decline with 89 percent accuracy.
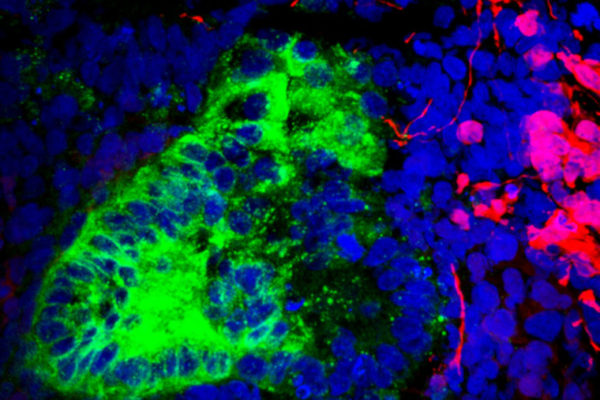
Brain, muscle cells found lurking in kidney organoids grown in lab
School of Medicine scientists have identified rogue cells – namely brain and muscle cells – lurking in kidney organoids, an indication that the “recipes” used to coax stem cells into becoming kidney cells inadvertently are churning out other cell types. The researchers also demonstrated they could prevent most of those wayward cells from forming, an approach that could be adopted by scientists working with other organoids, such as those of the brain, lung or heart.
New concussion recommendations for kids
The American Academy of Pediatrics has updated its concussion recommendations to support children and teens engaging in light physical activity and returning to school as they recover. The School of Medicine’s Mark Halstead, MD, was lead author of the report, which also advises against complete removal of electronic devices.
Cardiovascular disease, Alzheimer’s genetically linked
In the largest genetic study of Alzheimer’s disease, researchers at the School of Medicine and the University of California, San Francisco, have found that genes that increase risk of cardiovascular disease also heighten the risk for Alzheimer’s.
View More Stories