Black holes are topic of 2014 Robert M. Walker Distinguished Lecture
The topic of the 2014 Robert M. Walker Distinguished Lecture the evening of Oct. 23 will be black holes. The speaker is Ramesh Narayan, a Harvard astrophysicist who has studied the event horizon and the spin of these celestial enigmas. The talk, which starts at 7 p. m. in Whitaker Hall on the Danforth Campus, is free and open to the public.
The dwindling stock of antibiotics, and what to do about it
Pharmaceutical companies have largely abandoned the business of discovering and developing antibiotics and our stock of these “miracle drugs” is beginning to shrink. Michael Kinch and his colleagues at Washington University in St. Louis are working to create new models for drug discovery that could replace the failed private enterprise model.
‘The process by which drugs are discovered and developed will be fundamentally different in the future’
Over the past several decades, Michael Kinch of Washington University in St. Louis says, the pharmaceutical industry has managed to dismantle itself. In a provocative series of articles and interviews, Kinch, the director of the Center for Research Innovation in Businessat the university, has been describing the history of this dismantling and its implications for the future of medicine.
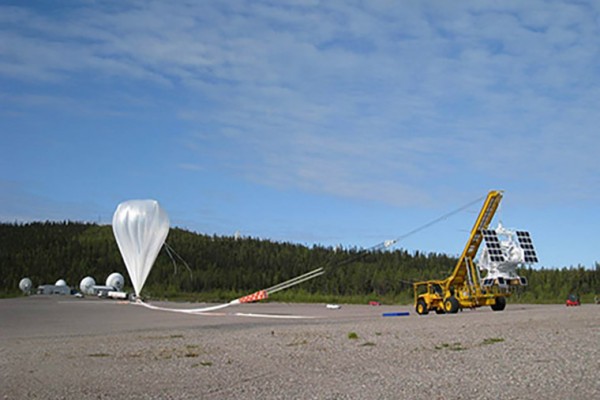
Balloon rise over Fort Sumner
In a few days, a balloon-borne telescope sensitive to the polarization of high-energy “hard” X rays will ascend to the edge of the atmosphere above Fort Sumner, N.M., to stare fixedly at black holes and other exotic astronomical objects. It will be carried aloft by a stratospheric balloon that will expand to a sphere large enough to hold a 747 jetliner the float height of 120,000 feet, three times the height at which commercial aircraft fly and on the edge of Earth’s atmosphere. Launching the balloon is not child’s play.
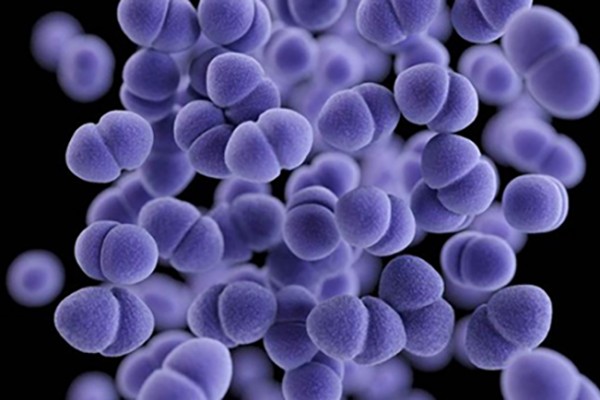
Zombie bacteria are nothing to be afraid of
Scientists at Washington University in St. Louis have obtained the first experimental evidence that there are at least two fail-safe points in the bacterial cell cycle. If the fail-safes are activated, the cell is forced to exit the cell cycle forever. It then enters a zombie-like state and is unable to reproduce
even under the most favorable of conditions. Drugs that trigger the fail-safes are already under development.
Scientists map the ‘editing marks’ on fly, worm, human genomes
In the Aug. 28 issue of the journal Nature, a multi-institution research network called modENCODE (the Model Organism ENCylopedia Of DNA Elements) published three major papers that map and compare the genomes and epigenomes of humans and two model
organisms, the fly, D. melanogaster, and the worm, C. elegans, in unprecedented detail. The fly and worm could serve as model organisms for screening drugs and micronutrients that might alter the epigenome, which is implicated in many diseases.
Experiments explain why some liquids are ‘fragile’ and others are ‘strong’
Only recently has it become possible to accurately “see” the structure of a liquid. Using X-rays and a high-tech apparatus that holds liquids without a container, a physicist at Washington University in St. Louis has compared the behavior of glass-forming liquids as they approach the glass transition. The results are the strongest demonstration yet that bulk properties like viscosity are linked to microscopic ones like structure.
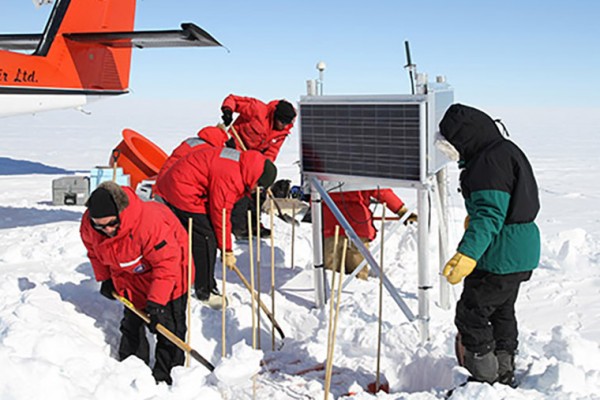
2010 Chilean earthquake triggered icequakes in Antarctica
In March 2010, the ice sheets in Antarctica vibrated a bit more than usual as a surface wave from an 8.8-magnitude earthquake in Chile 3,000 kilometers away passed through the ice. Powerful earthquakes were known to trigger secondary quakes along faults in land; this was the first observation of triggered quakes in the ice. Washington University in St. Louis seismologist Doug Wiens says the finding is one of several discoveries made possible by POLENET, an array of seismic stations that reaches for the first time into the interior of Antarctica.
Can large introductory science courses teach students to learn effectively?
In the past 10 years an active-learning course, called “Active Physics,” has gradually displaced lecture-based introductory courses in physics at Washington University in St. Louis. But are active-learning techniques effective when they are scaled up to large classes? A comprehensive three-year evaluation suggests that “Active Physics” consistently produces more proficient and confident students than the lecture courses it is replacing.
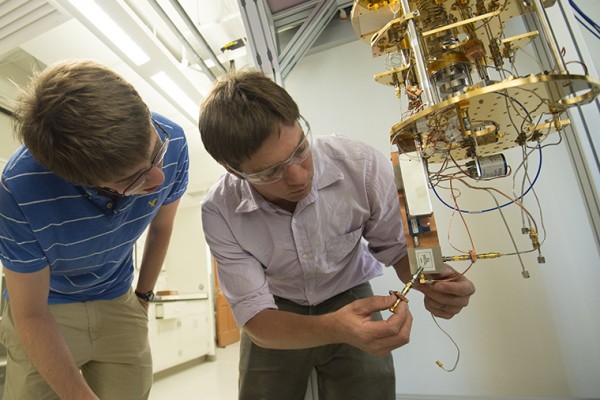
Finding quantum lines of desire
What paths do quantum particles, such as atoms or photons, follow through quantum state space? Kater Murch of Washington University in St. Louis has used a superconducting quantum device to continuously and repeatedly record the paths the device took through quantum state space. From the cobweb of a million paths, a most likely path between two quantum states emerged, much as social trails emerge as people round off corners or cut across lawns between buildings. The research is featured on the cover of the July 31 issue of Nature.
View More Stories