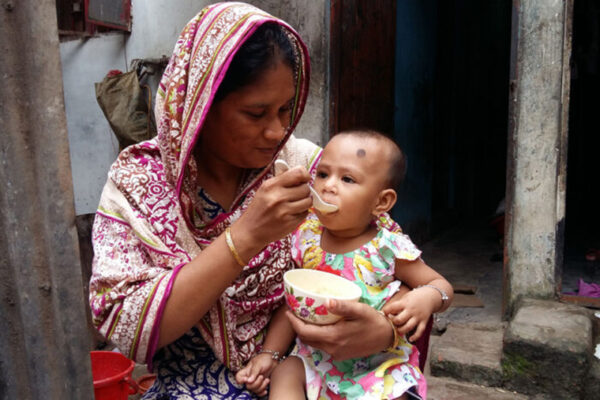
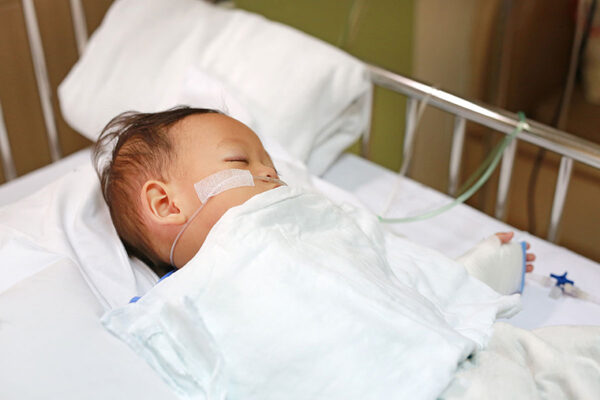
For malnourished children, a new type of microbiome-directed food boosts growth
A new study shows that a therapeutic food designed to repair the gut microbiomes of malnourished children is better than standard therapy in supporting their growth. The study was led by researchers at the School of Medicine and was published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
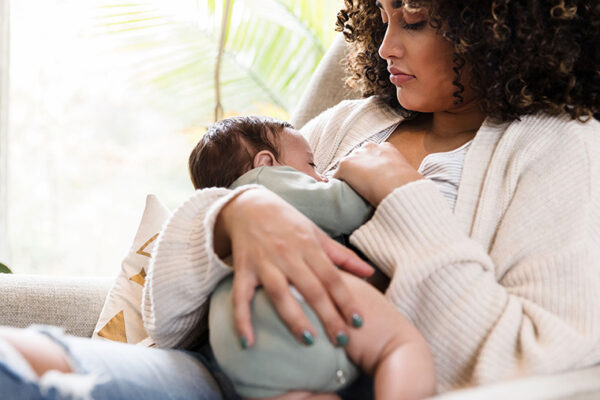
For breastfeeding moms, COVID-19 vaccinations may also protect babies
New research from Washington University School of Medicine suggests that nursing mothers who receive a COVID-19 vaccine may also protect their babies from the virus.
Study predicts which kids hospitalized with RSV likely to worsen
Children hospitalized with breathing problems due to infection with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are likely to get sicker and remain hospitalized if they have high levels of defective copies of the virus, according to a new study by researchers at the School of Medicine.
Mice with hallucination-like behaviors reveal insight into psychotic illness
A computer game that induces mice to experience hallucination-like events could be a key to understanding the neurobiological roots of psychosis, according to a School of Medicine study.
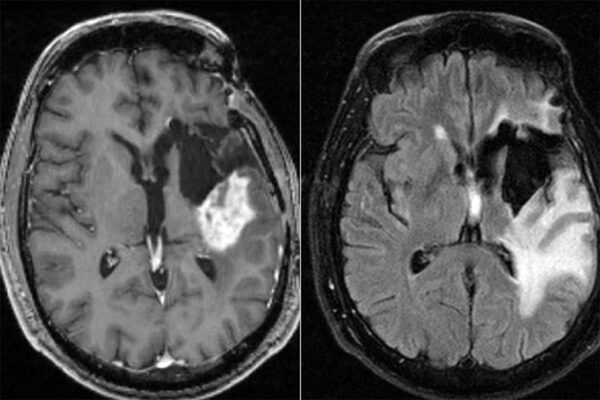
Chemo for glioblastoma may work better in morning than evening
A new study from Washington University suggests that a minor adjustment to the current standard treatment — giving chemotherapy in the morning rather than the evening — could add a few months to patients’ survival.
Scientists find genetic link to clogged arteries
A new study from the School of Medicine has identified a gene — called SVEP1 — that makes a protein that influences the risk of coronary artery disease independent of cholesterol.
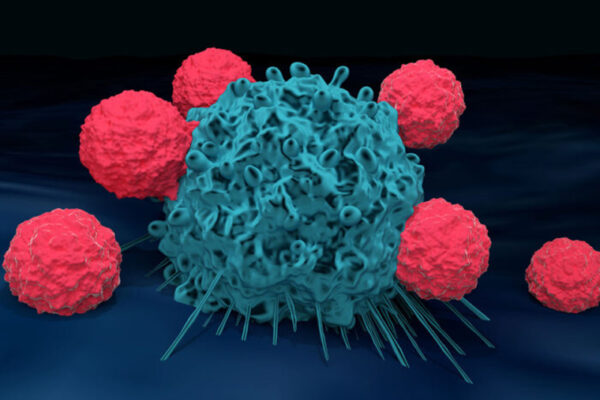
Zika virus helps destroy deadly brain cancer in mice
Zika virus can activate immune cells to destroy an aggressive brain cancer in mice, giving a powerful boost to an immunotherapy drug and sparking long-lasting immunological memory, according to a study from School of Medicine researchers.
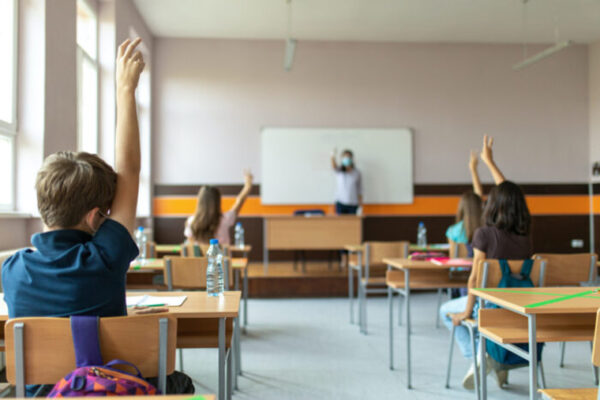
COVID-19 transmission rare in schools with safety measures
Wearing masks, social distancing and frequent hand-washing have kept in-school COVID-19 transmission low, according to results of a pilot study in Missouri involving the School of Medicine.
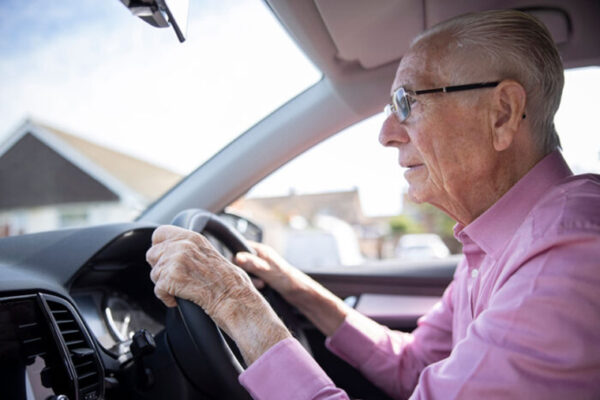
Can changes in driving habits predict cognitive decline in older adults?
Researchers at the School of Medicine have received three grants totaling more than $10 million to study the factors that contribute to deterioration in driving skills in older adults and to determine ways to identify people whose driving skills have begun to decline or are on the verge of slipping.
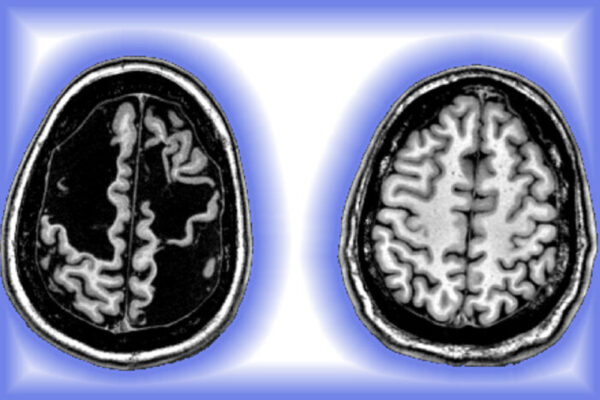
Brain rewires itself after injury ‘on the edge of what’s compatible with life’
Nico Dosenbach, MD, PhD, at the School of Medicine, conducted research over six years on a patient who suffered a stroke as a newborn. The case study show “the brain’s remarkable resiliency to rewire itself.”
View More Stories