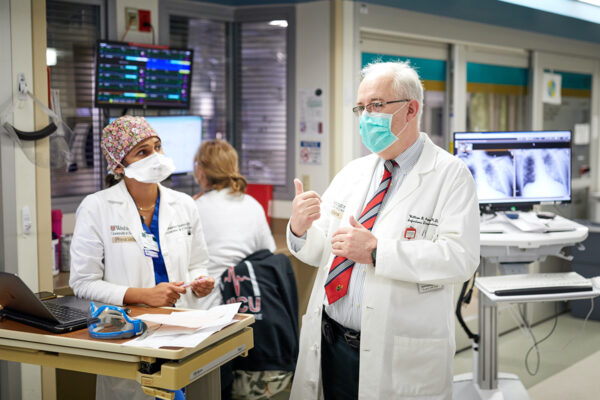
Immune modulator drugs for COVID-19 focus of major NIH clinical trial
A new, international phase 3 clinical trial led by the Washington University School of Medicine and funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), will investigate the potential of three drugs to tame a dangerous inflammatory response seen in some COVID-19 patients.
Role of gut viruses in inflammatory bowel disease is focus of $8.5 million grant
School of Medicine researchers have received an $8.5 million grant to study the role of gut viruses in inflammatory bowel disease. Tools developed in the course of the project could accelerate research into other roles of the virome in health and disease.
Racial differences in Alzheimer’s research focus of $15 million grant
A new grant for research at the School of Medicine focuses on brain scans and other markers of Alzheimer’s. The aim is to establish whether early markers of disease in white populations also apply to African Americans.
New discovery could help improve cancer vaccines
New research — co-led by Washington University School of Medicine — has identified the most important features of cancer cells’ protein fragments, which can help distinguish the tumor from healthy tissue, enabling researchers to design better immunotherapies, including vaccines.
Crisis response fund assists students, employees
The university’s crisis response fund will continue to support employees affected by the COVID-19 crisis. Applications for assistance open Monday, Oct. 12, and will remain open through Oct. 30. The fund already has distributed support to student applicants this fall.
‘Reflections’ event encourages university to come together
The Washington University in St. Louis community is invited to gather together virtually at noon Thursday, Oct. 8, for “Reflections: Remember & Recommit,” an event that will provide a space for grief and hope during this extraordinary time.
Cerebral palsy also has genetic underpinnings
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis and their colleagues at other institutions have identified mutations in single genes that can be responsible for at least some cases of cerebral palsy.
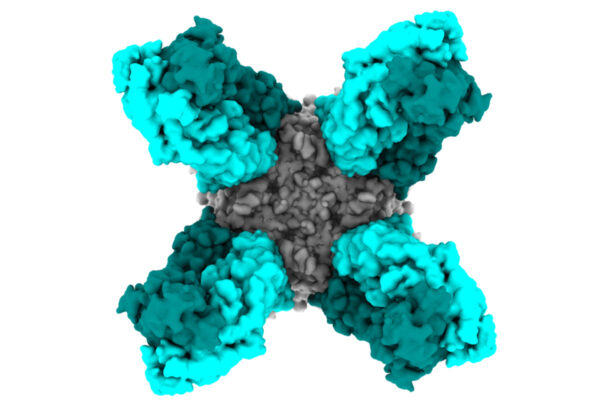
Antibodies protect against wide range of influenza B virus strains
Researchers have identified two antibodies that protect mice against lethal infections of influenza B virus. Together with an antibody that targets influenza A, the antibodies potentially could contribute to a drug to treat almost all flu cases.
Cancer centers to address pandemic’s impact on cancer prevention, treatment
A consortium of 17 U.S. cancer centers, including Siteman Cancer Center at Barnes-Jewish Hospital and Washington University School of Medicine, are working together to better understand the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic in delaying cancer detection, care and prevention.
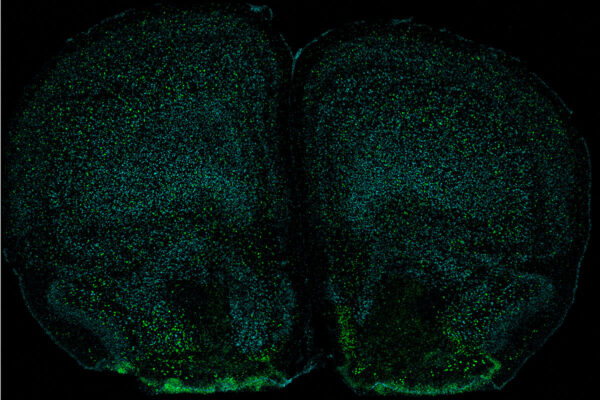
Immune system affects mind and body, study indicates
School of Medicine researchers have discovered that a molecule produced by the immune system acts on the brain to change the behavior of mice. The findings help illuminate a surprising mind-body connection.
View More Stories